Development of Pure Certified Reference Material of Cannabidiol
- PMID: 38474433
- PMCID: PMC10935364
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules29050921
Development of Pure Certified Reference Material of Cannabidiol
Abstract
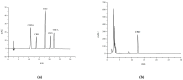
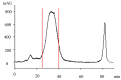
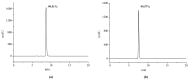
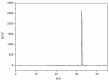
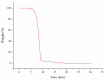
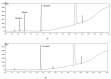
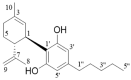
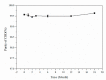
Cannabidiol (CBD) is the major functional component in hemp and has a broad range of pharmacological applications, such as analgesic, anti-epileptic, anti-anxiety, etc. Currently, CBD is widely used in pharmaceuticals, cosmetics, and food. To ensure the quality and safety of the products containing CBD, more and more related sample testing is being conducted, and the demand for CBD-certified reference material (CRM) has also sharply increased. However, there is currently a lack of relevant reference materials. In this paper, a simple method for preparing CBD CRM was established based on preparative liquid chromatography using crude hemp extract as a raw material. A qualitative analysis of CBD was performed using techniques such as ultraviolet absorption spectroscopy (UV), infrared spectroscopy (IR), mass spectrometry (MS), nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy (NMR), and differential scanning calorimetry (DSC). High-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) was used for the homogeneity and stability tests, and the data were analyzed using an F-test and a T-test, respectively. Then, eight qualified laboratories were chosen for the determination of a certified value using HPLC. The results show that the CBD CRM had excellent homogeneity and good stability for 18 months. The certified value was 99.57%, with an expanded uncertainty of 0.24% (p = 0.95, k = 2). The developed CBD CRM can be used for the detection and quality control of cannabidiol products.
Keywords: cannabidiol; certified reference material; preparative liquid chromatography.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Analysis of impurities of cannabidiol from hemp. Isolation, characterization and synthesis of cannabidibutol, the novel cannabidiol butyl analog.J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2019 Oct 25;175:112752. doi: 10.1016/j.jpba.2019.06.049. Epub 2019 Jul 12. J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2019. PMID: 31330283
-
Novel Intravenous Nanoemulsions Based on Cannabidiol-Enriched Hemp Oil-Development and Validation of an HPLC-DAD Method for Cannabidiol Determination.Molecules. 2025 Jan 12;30(2):278. doi: 10.3390/molecules30020278. Molecules. 2025. PMID: 39860148 Free PMC article.
-
[Research and development of certified reference material of swertioside].Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2020 Feb;45(4):955-960. doi: 10.19540/j.cnki.cjcmm.20191111.202. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2020. PMID: 32237499 Chinese.
-
Synthetic Strategies for (-)-Cannabidiol and Its Structural Analogs.Chem Asian J. 2019 Nov 4;14(21):3749-3762. doi: 10.1002/asia.201901179. Epub 2019 Oct 8. Chem Asian J. 2019. PMID: 31529613 Review.
-
Is cannabidiol a scheduled controlled substance? Origin makes the difference.Drug Discov Today. 2020 Apr;25(4):628-632. doi: 10.1016/j.drudis.2020.02.001. Epub 2020 Feb 13. Drug Discov Today. 2020. PMID: 32062008 Review.
Cited by
-
Impact of O-H···π Hydrogen Bond on IR and NMR Parameters of Cannabidiol: Theoretical and Experimental Study.Molecules. 2025 Jun 14;30(12):2591. doi: 10.3390/molecules30122591. Molecules. 2025. PMID: 40572554 Free PMC article.
-
Recent HPLC-UV Approaches for Cannabinoid Analysis: From Extraction to Method Validation and Quantification Compliance.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2025 May 24;18(6):786. doi: 10.3390/ph18060786. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40573182 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Development of purity certified reference materials to establish metrological traceability for the measurement of nitroimidazoles in agricultural products.Anal Bioanal Chem. 2024 Nov;416(28):6437-6449. doi: 10.1007/s00216-024-05530-3. Epub 2024 Sep 19. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2024. PMID: 39297935
References
-
- Krauke Y., Monks K. Purification of Cannabidiol from CBD Oil by Preparative HPLC. Knauer Wissenschaftliche Geräte GmbH, VPH0074 Application Note 2020. [(accessed on 20 November 2023)]. Available online: https://api.semanticscholar.org/CorpusID:233305754.
-
- Beal K. Considerations in the addition of cannabis to chocolate. Curr. Opin. Food Sci. 2019;28:14–17. doi: 10.1016/j.cofs.2019.02.007. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

