Marine-Derived Bisindoles for Potent Selective Cancer Drug Discovery and Development
- PMID: 38474445
- PMCID: PMC10935119
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules29050933
Marine-Derived Bisindoles for Potent Selective Cancer Drug Discovery and Development
Abstract
Marine-derived bisindoles exhibit structural diversity and exert anti-cancer influence through multiple mechanisms. Comprehensive research has shown that the development success rate of drugs derived from marine natural products is four times higher than that of other natural derivatives. Currently, there are 20 marine-derived drugs used in clinical practice, with 11 of them demonstrating anti-tumor effects. This article provides a thorough review of recent advancements in anti-tumor exploration involving 167 natural marine bisindole products and their derivatives. Not only has enzastaurin entered clinical practice, but there is also a successfully marketed marine-derived bisindole compound called midostaurin that is used for the treatment of acute myeloid leukemia. In summary, investigations into the biological activity and clinical progress of marine-derived bisindoles have revealed their remarkable selectivity, minimal toxicity, and efficacy against various cancer cells. Consequently, they exhibit immense potential in the field of anti-tumor drug development, especially in the field of anti-tumor drug resistance. In the future, these compounds may serve as promising leads in the discovery and development of novel cancer therapeutics.
Keywords: anticancer drug; antitumor activity; bisindole alkaloids; cancer; marine natural products.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
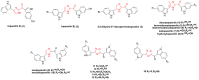
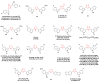
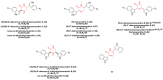
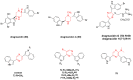
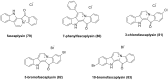
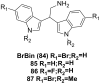

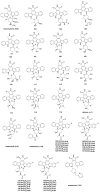
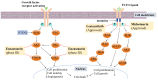
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

