Utilizing Extracellular Vesicles for Eliminating 'Unwanted Molecules': Harnessing Nature's Structures in Modern Therapeutic Strategies
- PMID: 38474460
- PMCID: PMC10935043
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules29050948
Utilizing Extracellular Vesicles for Eliminating 'Unwanted Molecules': Harnessing Nature's Structures in Modern Therapeutic Strategies
Abstract
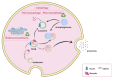
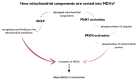
Extracellular vesicles (EVs) are small phospholipid bilayer-bond structures released by diverse cell types into the extracellular environment, maintaining homeostasis of the cell by balancing cellular stress. This article provides a comprehensive overview of extracellular vesicles, their heterogeneity, and diversified roles in cellular processes, emphasizing their importance in the elimination of unwanted molecules. They play a role in regulating oxidative stress, particularly by discarding oxidized toxic molecules. Furthermore, endoplasmic reticulum stress induces the release of EVs, contributing to distinct results, including autophagy or ER stress transmission to following cells. ER stress-induced autophagy is a part of unfolded protein response (UPR) and protects cells from ER stress-related apoptosis. Mitochondrial-derived vesicles (MDVs) also play a role in maintaining homeostasis, as they carry damaged mitochondrial components, thereby preventing inflammation. Moreover, EVs partake in regulating aging-related processes, and therefore they can potentially play a crucial role in anti-aging therapies, including the treatment of age-related diseases such as Alzheimer's disease or cardiovascular conditions. Overall, the purpose of this article is to provide a better understanding of EVs as significant mediators in both physiological and pathological processes, and to shed light on their potential for therapeutic interventions targeting EV-mediated pathways in various pathological conditions, with an emphasis on age-related diseases.
Keywords: age-related diseases; aging process; autophagy; endoplasmic reticulum stress; extracellular vesicles; mitochondrial-derived vesicles; oxidative stress.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Interactions between endoplasmic reticulum stress and extracellular vesicles in multiple diseases.Front Immunol. 2022 Aug 11;13:955419. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.955419. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 36032078 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Oligodendroglia-derived extracellular vesicles activate autophagy via LC3B/BAG3 to protect against oxidative stress with an enhanced effect for HSPB8 enriched vesicles.Cell Commun Signal. 2022 May 5;20(1):58. doi: 10.1186/s12964-022-00863-x. Cell Commun Signal. 2022. PMID: 35513867 Free PMC article.
-
Exosomes, autophagy and ER stress pathways in human diseases: Cross-regulation and therapeutic approaches.Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis. 2022 Oct 1;1868(10):166484. doi: 10.1016/j.bbadis.2022.166484. Epub 2022 Jul 8. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis. 2022. PMID: 35811032 Review.
-
Mitochondrial Extracellular Vesicles (mitoEVs): Emerging mediators of cell-to-cell communication in health, aging and age-related diseases.Ageing Res Rev. 2024 Nov;101:102522. doi: 10.1016/j.arr.2024.102522. Epub 2024 Oct 5. Ageing Res Rev. 2024. PMID: 39369800 Review.
-
Lipotoxic stress alters the membrane lipid profile of extracellular vesicles released by Huh-7 hepatocarcinoma cells.Sci Rep. 2021 Feb 25;11(1):4613. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-84268-9. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 33633289 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Role of Redox Homeostasis in the Communication Between Brain and Liver Through Extracellular Vesicles.Antioxidants (Basel). 2024 Dec 6;13(12):1493. doi: 10.3390/antiox13121493. Antioxidants (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39765821 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mesenchymal stem cells derived exosomes: a new era in cardiac regeneration.Stem Cell Res Ther. 2025 Jan 23;16(1):16. doi: 10.1186/s13287-024-04123-2. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2025. PMID: 39849585 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A case for the study of native extracellular vesicles.Front Oncol. 2024 Jul 12;14:1430971. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2024.1430971. eCollection 2024. Front Oncol. 2024. PMID: 39091922 Free PMC article.
-
Beyond the Bubble: A Debate on microRNA Sorting Into Extracellular Vesicles.Lab Invest. 2025 Feb;105(2):102206. doi: 10.1016/j.labinv.2024.102206. Epub 2024 Dec 6. Lab Invest. 2025. PMID: 39647608 Review.
-
Exercise-Intervened Circulating Extracellular Vesicles Alleviate Oxidative Stress in Cerebral Microvascular Endothelial Cells Under Hypertensive Plus Hypoxic Conditions.Antioxidants (Basel). 2025 Jan 10;14(1):77. doi: 10.3390/antiox14010077. Antioxidants (Basel). 2025. PMID: 39857411 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

