Neuroprotective Effects of Polysaccharides and Gallic Acid from Amauroderma rugosum against 6-OHDA-Induced Toxicity in SH-SY5Y Cells
- PMID: 38474465
- PMCID: PMC10934954
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules29050953
Neuroprotective Effects of Polysaccharides and Gallic Acid from Amauroderma rugosum against 6-OHDA-Induced Toxicity in SH-SY5Y Cells
Abstract
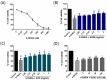
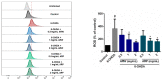
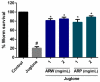
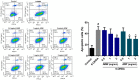
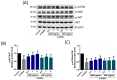
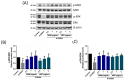
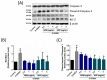
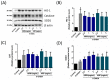
The pharmacological activity and medicinal significance of Amauroderma rugosum (AR) have rarely been documented. We examined the antioxidant and neuroprotective effects of AR on 6-hydroxydopamine (6-OHDA)-induced neurotoxicity in an SH-SY5Y human neuroblastoma cell model of Parkinson's disease (PD) and explored the active ingredients responsible for these effects. The results showed that the AR aqueous extract could scavenge reactive oxygen species and reduce SH-SY5Y cell death induced by 6-OHDA. In addition, the AR aqueous extract increased the survival of Caenorhabditis elegans upon juglone-induced toxicity. Among the constituents of AR, only polysaccharides and gallic acid exhibited antioxidant and neuroprotective effects. The AR aqueous extract reduced apoptosis and increased the expression of phospho-Akt, phospho-mTOR, phospho-MEK, phospho-ERK, and superoxide dismutase-1 in 6-OHDA-treated SH-SY5Y cells. The polysaccharide-rich AR extract was slightly more potent than the aqueous AR extract; however, it did not affect the expression of phospho-Akt or phospho-mTOR. In conclusion, the AR aqueous extract possessed antioxidant and neuroprotective properties against 6-OHDA-induced toxicity in SH-SY5Y cells. The mechanism of action involves the upregulation of the Akt/mTOR and MEK/ERK-dependent pathways. These findings indicate the potential utility of AR and its active ingredients in preventing or treating neurodegenerative disorders associated with oxidative stress such as PD.
Keywords: Amauroderma rugosum; antioxidant; gallic acid; neuroprotective; polysaccharides.
Conflict of interest statement
Author Timothy Man-Yau Cheung was employed by the company Tian Ran Healthcare Limited. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

