Enzymes in "Green" Synthetic Chemistry: Laccase and Lipase
- PMID: 38474502
- PMCID: PMC10934700
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules29050989
Enzymes in "Green" Synthetic Chemistry: Laccase and Lipase
Abstract
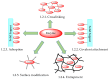
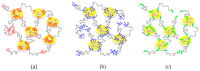
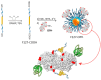
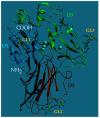
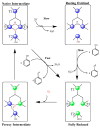
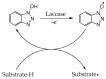
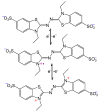
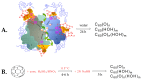
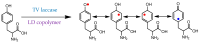
Enzymes play an important role in numerous natural processes and are increasingly being utilized as environmentally friendly substitutes and alternatives to many common catalysts. Their essential advantages are high catalytic efficiency, substrate specificity, minimal formation of byproducts, and low energy demand. All of these benefits make enzymes highly desirable targets of academic research and industrial development. This review has the modest aim of briefly overviewing the classification, mechanism of action, basic kinetics and reaction condition effects that are common across all six enzyme classes. Special attention is devoted to immobilization strategies as the main tools to improve the resistance to environmental stress factors (temperature, pH and solvents) and prolong the catalytic lifecycle of these biocatalysts. The advantages and drawbacks of methods such as macromolecular crosslinking, solid scaffold carriers, entrapment, and surface modification (covalent and physical) are discussed and illustrated using numerous examples. Among the hundreds and possibly thousands of known and recently discovered enzymes, hydrolases and oxidoreductases are distinguished by their relative availability, stability, and wide use in synthetic applications, which include pharmaceutics, food and beverage treatments, environmental clean-up, and polymerizations. Two representatives of those groups-laccase (an oxidoreductase) and lipase (a hydrolase)-are discussed at length, including their structure, catalytic mechanism, and diverse usage. Objective representation of the current status and emerging trends are provided in the main conclusions.
Keywords: enzymes; immobilization; laccase; linear-dendritic copolymers; lipase; polymerization; polyphenols; wine making; “green” chemistry.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of the data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures
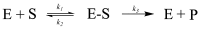

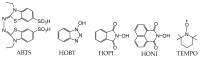

References
-
- Anwar A., Imran M., Iqbal H.M.N. Smart chemistry and applied perceptions of enzyme-coupled nano-engineered assemblies to meet future biocatalytic challenges. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2023;493:215329. doi: 10.1016/j.ccr.2023.215329. - DOI
-
- Payen P.A., Persoz J.F. Memoir on diastase, the principal products of its reactions, and their applications to the industrial arts. Ann. Chim. Phys. 1833;53:73–92.
-
- Kühne W. Über das Verhalten verschiedener organisirter und sog. Ungeformter Fermente. Verh. Heidelb. Naturhist.-Med. Ver. Neue Folge. 1877;1:190–193.
-
- Sumner J.B. The Isolation and Crystallization of the Enzyme Urease. J. Biol. Chem. 1926;69:435–441. doi: 10.1016/S0021-9258(18)84560-4. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

