Precision Nutrition Unveiled: Gene-Nutrient Interactions, Microbiota Dynamics, and Lifestyle Factors in Obesity Management
- PMID: 38474710
- PMCID: PMC10935146
- DOI: 10.3390/nu16050581
Precision Nutrition Unveiled: Gene-Nutrient Interactions, Microbiota Dynamics, and Lifestyle Factors in Obesity Management
Abstract
Background: Obesity is a complex metabolic disorder that is associated with several diseases. Recently, precision nutrition (PN) has emerged as a tailored approach to provide individualised dietary recommendations.
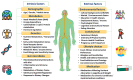
Aim: This review discusses the major intrinsic and extrinsic components considered when applying PN during the management of obesity and common associated chronic conditions.
Results: The review identified three main PN components: gene-nutrient interactions, intestinal microbiota, and lifestyle factors. Genetic makeup significantly contributes to inter-individual variations in dietary behaviours, with advanced genome sequencing and population genetics aiding in detecting gene variants associated with obesity. Additionally, PN-based host-microbiota evaluation emerges as an advanced therapeutic tool, impacting disease control and prevention. The gut microbiome's composition regulates diverse responses to nutritional recommendations. Several studies highlight PN's effectiveness in improving diet quality and enhancing adherence to physical activity among obese patients. PN is a key strategy for addressing obesity-related risk factors, encompassing dietary patterns, body weight, fat, blood lipids, glucose levels, and insulin resistance.
Conclusion: PN stands out as a feasible tool for effectively managing obesity, considering its ability to integrate genetic and lifestyle factors. The application of PN-based approaches not only improves current obesity conditions but also holds promise for preventing obesity and its associated complications in the long term.
Keywords: genetics; lifestyle factors; microbiome; obesity; precision nutrition; translational medicine.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Chen L., Zhernakova D.V., Kurilshikov A., Andreu-Sánchez S., Wang D., Augustijn H.E., Vich Vila A., Weersma R.K., Medema M.H., Netea M.G., et al. Influence of the Microbiome, Diet and Genetics on Inter-Individual Variation in the Human Plasma Metabolome. Nat. Med. 2022;28:2333–2343. doi: 10.1038/s41591-022-02014-8. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

