Is There a Role of Beetroot Consumption on the Recovery of Oxidative Status and Muscle Damage in Ultra-Endurance Runners?
- PMID: 38474711
- PMCID: PMC10934908
- DOI: 10.3390/nu16050583
Is There a Role of Beetroot Consumption on the Recovery of Oxidative Status and Muscle Damage in Ultra-Endurance Runners?
Abstract
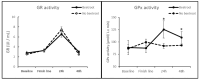
(1) Background: Ultra-endurance exercise involves a high physical impact, resulting in muscle damage, inflammatory response and production of free radicals that alter the body's oxidative state. Supplementation with antioxidants, such as beetroot, may improve recovery in ultra-endurance runners. The aim of this study was to determine whether there is a correlation between beetroot intake and recovery of serum oxidative status, inflammatory response and muscle damage parameters after an ultra-endurance race. (2) Methods: An observational and longitudinal study was conducted by means of surveys and blood samples collected from 32 runners during the IX Penyagolosa Trails CSP®® race and the two following days. The variables C-reactive protein (CRP), lactate dehydrogenase (LDH), creatine kinase (CK), the activity of the antioxidant enzymes glutathione peroxidase (GPx) and glutathione reductase (GR) as well as the oxidative damage markers malondialdehyde (MDA), carbonyl groups (CG) and loss of muscle strength using the squat jump (SJ) test were analyzed to discriminate whether beetroot consumption can modulate the recovery of ultra-trail runners. (3) Results: Significant differences were observed between runners who ingested beetroot and those who did not, in terms of oxidative status, specifically in serum GPx activity at 24 and 48 h, muscle damage variables CK and LDH and regarding the SJ test results at the finish line. Therefore, the intake of supplements containing beetroot positively influences the recovery of serum oxidative status and muscle damage after ultra-endurance running.
Keywords: antioxidants; muscle damage; oxidative stress; ultra-endurance sport.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Devrim-Lanpir A., Bilgic P., Kocahan T., Deliceoğlu G., Rosemann T., Knechtle B. Total Dietary Antioxidant Intake Including Polyphenol Content: Is It Capable to Fight against Increased Oxidants within the Body of Ultra-Endurance Athletes? Nutrients. 2020;12:1877. doi: 10.3390/nu12061877. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Viljoen C., du Toit E., van Niekerk T., Mashaba S., Ndaba Z., Verster M., Bellingan A., Ramagole D., Jansen van Rensburg A., Botha T., et al. Training for shorter ultra-trail races results in a higher injury rate, a more diverse injury profile, and more severe injuries: 2022 Mac ultraraces. Phys. Ther. Sport. 2023;65:7–13. doi: 10.1016/j.ptsp.2023.10.004. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

