Immuno-Enhancing Effects of Galium aparine L. in Cyclophosphamide-Induced Immunosuppressed Animal Models
- PMID: 38474724
- PMCID: PMC10934713
- DOI: 10.3390/nu16050597
Immuno-Enhancing Effects of Galium aparine L. in Cyclophosphamide-Induced Immunosuppressed Animal Models
Abstract
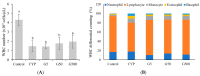
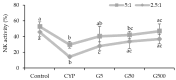
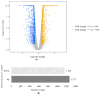
This study investigates the immunomodulatory potential of Galium aparine L. (GAE) in immunodeficient animals. In this study, animals were categorized into five groups: the normal group, CYP group (cyclophosphamide intraperitoneal injection), GA5 group (cyclophosphamide + 5 μg GAE), GA50 group (cyclophosphamide + 50 μg GAE), and GA500 group (cyclophosphamide + 500 μg GAE). The CYP group exhibited significantly reduced spleen weights compared to the normal group, while the groups obtaining GAE displayed a dose-dependent increase in spleen weight. Furthermore, the GAE demonstrated dose-dependent enhancement of splenocyte proliferating activity, with significant increases observed in both LPS and ConA-induced assays. NK cell activity significantly increased in the GA50 and GA500 groups compared to the CYP group. Cytokine analysis revealed a significant increase in IL-6, TNF-α, and IFN-γ levels in ConA-induced splenocytes treated with GAE. Gene expression analysis identified 2434 DEG genes in the extract groups. Notable genes, such as Entpd1, Pgf, Thdb, Syt7, Sqor, and Rsc1al, displayed substantial differences in individual gene expression levels, suggesting their potential as target genes for immune enhancement. In conclusion, Galium aparine L. extract exhibits immunomodulatory properties. The observed gene expression changes further support the potential of Galium aparine L. extract as a natural agent for immune augmentation.
Keywords: Galium aparine L. extract; NK cell activity; cyclophosphamide; immune stimulation; splenocyte proliferation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Phytochemical Profiles and In Vitro Immunomodulatory Activity of Ethanolic Extracts from Galium aparine L.Plants (Basel). 2019 Nov 25;8(12):541. doi: 10.3390/plants8120541. Plants (Basel). 2019. PMID: 31775336 Free PMC article.
-
Immuno-enhancement effects of Platycodon grandiflorum extracts in splenocytes and a cyclophosphamide-induced immunosuppressed rat model.BMC Complement Altern Med. 2019 Nov 21;19(1):322. doi: 10.1186/s12906-019-2724-0. BMC Complement Altern Med. 2019. PMID: 31752816 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of Galium aparine extract on the cell viability, cell cycle and cell death in breast cancer cell lines.J Ethnopharmacol. 2016 Jun 20;186:305-310. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2016.04.007. Epub 2016 Apr 13. J Ethnopharmacol. 2016. PMID: 27085941
-
Indole-3-acetic acid and auxin herbicides up-regulate 9-cis-epoxycarotenoid dioxygenase gene expression and abscisic acid accumulation in cleavers (Galium aparine): interaction with ethylene.J Exp Bot. 2007;58(6):1497-503. doi: 10.1093/jxb/erm011. Epub 2007 Feb 21. J Exp Bot. 2007. PMID: 17317672
-
Immunomodulatory activity of Lactobacillus plantarum KLDS1.0318 in cyclophosphamide-treated mice.Food Nutr Res. 2018 Mar 21;62. doi: 10.29219/fnr.v62.1296. eCollection 2018. Food Nutr Res. 2018. PMID: 30026678 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
A Review of Phytochemical and Pharmacological Studies on Galium verum L., Rubiaceae.Molecules. 2025 Apr 21;30(8):1856. doi: 10.3390/molecules30081856. Molecules. 2025. PMID: 40333892 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Immunoenhancing effects of Gynostemma Pentaphyllum Extract on mucosal immunity against porcine epidemic diarrhea virus.Front Vet Sci. 2025 Aug 22;12:1636663. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2025.1636663. eCollection 2025. Front Vet Sci. 2025. PMID: 40919038 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

