Application of Nanoparticles in Human Nutrition: A Review
- PMID: 38474764
- PMCID: PMC10934945
- DOI: 10.3390/nu16050636
Application of Nanoparticles in Human Nutrition: A Review
Abstract
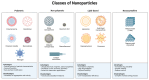
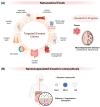
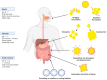
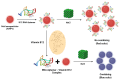
Nanotechnology in human nutrition represents an innovative advance in increasing the bioavailability and efficiency of bioactive compounds. This work delves into the multifaceted dietary contributions of nanoparticles (NPs) and their utilization for improving nutrient absorption and ensuring food safety. NPs exhibit exceptional solubility, a significant surface-to-volume ratio, and diameters ranging from 1 to 100 nm, rendering them invaluable for applications such as tissue engineering and drug delivery, as well as elevating food quality. The encapsulation of vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants within NPs introduces an innovative approach to counteract nutritional instabilities and low solubility, promoting human health. Nanoencapsulation methods have included the production of nanocomposites, nanofibers, and nanoemulsions to benefit the delivery of bioactive food compounds. Nutrition-based nanotechnology and nanoceuticals are examined for their economic viability and potential to increase nutrient absorption. Although the advancement of nanotechnology in food demonstrates promising results, some limitations and concerns related to safety and regulation need to be widely discussed in future research. Thus, the potential of nanotechnology could open new paths for applications and significant advances in food, benefiting human nutrition.
Keywords: bioactive compounds; cancer; health human; nanotechnology; nutraceuticals; phytochemicals.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Nanoencapsulation of Promising Bioactive Compounds to Improve Their Absorption, Stability, Functionality and the Appearance of the Final Food Products.Molecules. 2021 Mar 11;26(6):1547. doi: 10.3390/molecules26061547. Molecules. 2021. PMID: 33799855 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nanotechnology Approaches for Increasing Nutrient Bioavailability.Adv Food Nutr Res. 2017;81:1-30. doi: 10.1016/bs.afnr.2016.12.008. Epub 2017 Jan 24. Adv Food Nutr Res. 2017. PMID: 28317602 Review.
-
Bioavailability of nanotechnology-based bioactives and nutraceuticals.Adv Food Nutr Res. 2019;88:235-273. doi: 10.1016/bs.afnr.2019.02.014. Epub 2019 Apr 1. Adv Food Nutr Res. 2019. PMID: 31151725
-
Bioactive-loaded nanodelivery systems for the feed and drugs of livestock; purposes, techniques and applications.Adv Colloid Interface Sci. 2022 Oct;308:102772. doi: 10.1016/j.cis.2022.102772. Epub 2022 Sep 6. Adv Colloid Interface Sci. 2022. PMID: 36087561 Review.
-
Deciphering the importance of nanoencapsulation to improve the availability of bioactive molecules in food sources to the human body.Food Chem. 2025 Feb 1;464(Pt 3):141762. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2024.141762. Epub 2024 Oct 24. Food Chem. 2025. PMID: 39509889 Review.
Cited by
-
Advances and prospects of precision nanomedicine in personalized tumor theranostics.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2024 Dec 5;12:1514399. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2024.1514399. eCollection 2024. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2024. PMID: 39712574 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Revolutionizing Veterinary Medicine: The Role of Nanoparticles in Advancing Animal Health, Nutrition and Disease Management.Vet Med Sci. 2025 Sep;11(5):e70528. doi: 10.1002/vms3.70528. Vet Med Sci. 2025. PMID: 40747873 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Microencapsulation of Essential Oils and Oleoresins: Applications in Food Products.Foods. 2024 Nov 29;13(23):3873. doi: 10.3390/foods13233873. Foods. 2024. PMID: 39682947 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Dietary Polyphenols, Plant Metabolites, and Allergic Disorders: A Comprehensive Review.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2024 May 22;17(6):670. doi: 10.3390/ph17060670. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38931338 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Inulin Improves the Redox Response in Rats Fed a Diet Containing Recommended Copper Nanoparticle (CuNPs) Levels, While Pectin or Psyllium in Rats Receive Excessive CuNPs Levels in the Diet.Antioxidants (Basel). 2025 Jun 8;14(6):695. doi: 10.3390/antiox14060695. Antioxidants (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40563326 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ndlovu N., Mayaya T., Muitire C., Munyengwa N. Nanotechnology Applications in Crop Production and Food Systems. Int. J. Plant Breed. 2020;7:624–634.
-
- Brandelli A., Pinilla C.M.B., Lopes N.A. Nanotechnology in Food Preservation. Adv. Process. Technol. Bio-Based Nanosyst. Food. 2019;9:277–311. doi: 10.15740/has/fsrj/9.2/441-447. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

