Vitamin D Supplementation and Recurrence of Benign Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo
- PMID: 38474817
- PMCID: PMC10934290
- DOI: 10.3390/nu16050689
Vitamin D Supplementation and Recurrence of Benign Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo
Abstract
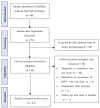
Positional vertigo manifests as a spinning sensation triggered by changes in head position relative to gravity. Benign paroxysmal positional vertigo (BPPV) is an inner ear disorder characterized by recurrent episodes of positional vertigo. The connection between vitamin D insufficiency/deficiency and the onset and recurrence of BPPV is established. This study aims to assess vitamin D as a recurring factor in BPPV and the efficacy of vitamin D supplementation in preventing its recurrence. A comprehensive literature review on the relationship between vitamin D and BPPV recurrence was conducted, searching PubMed, Embase, Web of Science, and article reference lists for studies published from 2020 to 2023. A total of 79 articles were initially identified through the search, with 12 of them being utilized in the study. Recurrence rates for BPPV varied from 13.7% to 23% for studies with follow-up less than 1 year and 13.3% to 65% for studies with follow-up equal to or exceeding 2 years. Risk factors for BPPV recurrence include advanced age, female sex, hypertension, diabetes mellitus, hyperlipidemia, osteoporosis, and vitamin D deficiency. While earlier studies did not establish a link between low vitamin D levels and initial BPPV occurrence, they did associate recurrent episodes with low vitamin D levels. Recent research indicates that vitamin D supplementation in BPPV patients with deficiency or insufficiency decreases both the numbers of relapsing patients and relapses per patient. To validate these findings across diverse populations, further randomized controlled studies with larger cohorts and extended follow-up durations are essential.
Keywords: benign paroxysmal positional vertigo; recurrence; supplementation; treatment; vitamin D.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The role of low levels of vitamin D as a co-factor in the relapse of benign paroxysmal positional vertigo (BPPV).Am J Otolaryngol. 2021 Nov-Dec;42(6):103134. doi: 10.1016/j.amjoto.2021.103134. Epub 2021 Jun 19. Am J Otolaryngol. 2021. PMID: 34166965
-
Prevention of recurrent benign paroxysmal positional vertigo with vitamin D supplementation: a meta-analysis.J Neurol. 2022 Feb;269(2):619-626. doi: 10.1007/s00415-020-09952-8. Epub 2020 Aug 7. J Neurol. 2022. PMID: 32767116 Review.
-
Association between vitamin D, vitamin D supplementation and benign paroxysmal positional vertigo: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Front Neurol. 2025 Apr 16;16:1560616. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2025.1560616. eCollection 2025. Front Neurol. 2025. PMID: 40308226 Free PMC article.
-
Reduction of recurrence rate of benign paroxysmal positional vertigo by treatment of severe vitamin D deficiency.Auris Nasus Larynx. 2016 Jun;43(3):237-41. doi: 10.1016/j.anl.2015.08.009. Epub 2015 Sep 16. Auris Nasus Larynx. 2016. PMID: 26386496
-
Effect of vitamin D supplementation on benign paroxysmal positional vertigo recurrence: A meta-analysis.Sci Prog. 2021 Apr-Jun;104(2):368504211024569. doi: 10.1177/00368504211024569. Sci Prog. 2021. PMID: 34128742 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Transcriptomic analysis reveals cross-talk genes between type 2 diabetes and recurrent benign paroxysmal positional vertigo.Heliyon. 2024 Jul 29;10(15):e35209. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e35209. eCollection 2024 Aug 15. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 39170394 Free PMC article.
-
Identifying key risk factors for the recurrence of benign paroxysmal positional vertigo following successful canalith repositioning maneuvers: a meta analysis.Eur J Med Res. 2025 Apr 10;30(1):262. doi: 10.1186/s40001-025-02482-x. Eur J Med Res. 2025. PMID: 40211383 Free PMC article.
-
Circulating levels of micronutrients and the risk of benign paroxysmal positional vertigo: A Mendelian randomization study.Heliyon. 2024 Oct 2;10(19):e38782. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e38782. eCollection 2024 Oct 15. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 39430529 Free PMC article.
-
Serum Otoconin-90 and Otolin-1 Concentrations in Benign Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo.Biomolecules. 2024 Oct 10;14(10):1279. doi: 10.3390/biom14101279. Biomolecules. 2024. PMID: 39456211 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical