Factors Influencing Duration of Breastfeeding: Insights from a Prospective Study of Maternal Health Literacy and Obstetric Practices
- PMID: 38474818
- PMCID: PMC10933905
- DOI: 10.3390/nu16050690
Factors Influencing Duration of Breastfeeding: Insights from a Prospective Study of Maternal Health Literacy and Obstetric Practices
Abstract
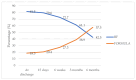
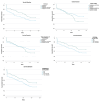
Numerous factors concerning early breastfeeding abandonment have been described, including health literacy (HL). This study's objective was to analyze factors related to early breastfeeding abandonment (<6 months). This prospective multicentric study examined the duration of breastfeeding at 6 months postpartum and was conducted in four different regions of Spain from January 2021 to January 2023. A total of 275 women participated in this study, which focused on maternal HL and obstetric practices. A decrease in the breastfeeding rate was observed from hospital discharge (n = 224, 81.5%) to the sixth month postpartum (n = 117, 42.5%). A Cox regression analysis revealed that inadequate HL levels, lack of mobilization during labour, and induced labour were significantly associated with early breastfeeding cessation (p = 0.022, p = 0.019, and p = 0.010, respectively). The results highlight that women with adequate HL had a 32% lower risk of early breastfeeding abandonment. In comparison, mobilization during labour and induction of labour were linked to a 32.4% reduction and a 53.8% increase in this risk, respectively. These findings emphasize the importance of considering obstetric and HL factors when addressing the breastfeeding duration, indicating opportunities for educational and perinatal care interventions.
Keywords: abandonment; breastfeeding; health literacy; nursing.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- World Health Organization (WHO) United Nations Children’s Fund (UNICEF) Protecting, Promoting and Supporting Breast-Feeding: The Special Role of Maternity Services/a Joint WHO/UNICEF Statement. World Health Organization; Geneva, Switzerland: 1989.
-
- World Health Organization. European Health Information Gateway % of Infants Breastfed at Age 6 Months. [(accessed on 23 January 2024)]. Available online: https://gateway.euro.who.int/en/indicators/hfa_616-7260-of-infants-breas....
-
- Instituto Nacional de Estadística (INE) Tipo de Lactancia Según Sexo y Clase Social Basada en la Ocupación de la Persona de Referencia. Población de 6 Meses a 4 Años. Encuesta Nacional de Salud España. [(accessed on 10 December 2023)]. Available online: https://www.ine.es/jaxi/Tabla.htm?path=/t15/p419/a2017/p06/l0/&file=0600....
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

