Effects of Visible Light on Gas Sensors: From Inorganic Resistors to Molecular Material-Based Heterojunctions
- PMID: 38475107
- PMCID: PMC10935338
- DOI: 10.3390/s24051571
Effects of Visible Light on Gas Sensors: From Inorganic Resistors to Molecular Material-Based Heterojunctions
Abstract
In the last two decades, many research works have been focused on enhancing the properties of gas sensors by utilising external triggers like temperature and light. Most interestingly, the light-activated gas sensors show promising results, particularly using visible light as an external trigger that lowers the power consumption as well as improves the stability, sensitivity and safety of the sensors. It effectively eliminates the possible damage to sensing material caused by high operating temperature or high energy light. This review summarises the effect of visible light illumination on both chemoresistors and heterostructure gas sensors based on inorganic and organic materials and provides a clear understanding of the involved phenomena. Finally, the fascinating concept of ambipolar gas sensors is presented, which utilised visible light as an external trigger for inversion in the nature of majority charge carriers in devices. This review should offer insight into the current technologies and offer a new perspective towards future development utilising visible light in light-assisted gas sensors.
Keywords: adsorption–desorption mechanism; conductometric transducers; heterojunctions; light effect; resistors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
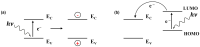

 ) and of target gas with holes (
) and of target gas with holes ( ), both and being photo-generated (b) (modified from [47]).
), both and being photo-generated (b) (modified from [47]).






Similar articles
-
In-situ construction of direct Z-scheme NiO/Bi2MoO6 heterostructure arrays with enhanced room temperature ether sensing properties under visible light irradiation.J Hazard Mater. 2023 Sep 15;458:131936. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2023.131936. Epub 2023 Jun 25. J Hazard Mater. 2023. PMID: 37385099
-
Light-Activated Metal Oxide Gas Sensors: A Review.Micromachines (Basel). 2017 Nov 18;8(11):333. doi: 10.3390/mi8110333. Micromachines (Basel). 2017. PMID: 30400523 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Light-assisted room temperature gas sensing performance and mechanism of direct Z-scheme MoS2/SnO2 crystal faceted heterojunctions.J Hazard Mater. 2022 Aug 15;436:129246. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2022.129246. Epub 2022 May 30. J Hazard Mater. 2022. PMID: 35739765
-
Increased Active Sites and Charge Transfer in the SnS2/TiO2 Heterostructure for Visible-Light-Assisted NO2 Sensing.ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2021 Nov 17;13(45):54152-54161. doi: 10.1021/acsami.1c16095. Epub 2021 Nov 4. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2021. PMID: 34734688
-
Light-Assisted Enhancement of Gas Sensing Property for Micro-Nanostructure Electronic Device: A Mini Review.Front Chem. 2021 Dec 24;9:811074. doi: 10.3389/fchem.2021.811074. eCollection 2021. Front Chem. 2021. PMID: 35004627 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Designing Bimetallic Sensors for Acetone Biomarker Detection.ACS Omega. 2025 Mar 25;10(13):12953-12960. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.4c09037. eCollection 2025 Apr 8. ACS Omega. 2025. PMID: 40224453 Free PMC article.
-
Enhanced Sensitivity in Photovoltaic 2D MoS2/Te Heterojunction VOC Sensors.Small. 2024 Dec;20(49):e2402464. doi: 10.1002/smll.202402464. Epub 2024 Jul 26. Small. 2024. PMID: 39058241 Free PMC article.
-
Excellent Room-Temperature NO2 Gas-Sensing Properties of TiO2-SnO2 Composite Thin Films Under Light Activation.Nanomaterials (Basel). 2025 Jun 5;15(11):871. doi: 10.3390/nano15110871. Nanomaterials (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40497920 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Yang Z., Dou X. Emerging and future possible strategies for enhancing 1D inorganic nanomaterials-based electrical sensors towards explosives vapours detection. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2016;26:2406–2425. doi: 10.1002/adfm.201504846. - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

