Mucoadhesive Polymeric Polyologels Designed for the Treatment of Periodontal and Related Diseases of the Oral Cavity
- PMID: 38475273
- PMCID: PMC10934824
- DOI: 10.3390/polym16050589
Mucoadhesive Polymeric Polyologels Designed for the Treatment of Periodontal and Related Diseases of the Oral Cavity
Abstract
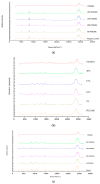
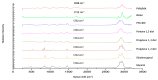
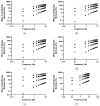
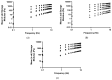
The study objective was to design and characterise herein unreported polyologels composed of a range of diol and triol solvents and polyvinyl methyl ether-co-maleic acid (PVM/MA) and, determine their potential suitability for the treatment of periodontal and related diseases in the oral cavity using suitable in vitro methodologies. Polyologel flow and viscoelastic properties were controlled by the choice of solvent and the concentration of polymer. At equivalent polymer concentrations, polyologels prepared with glycerol (a triol) exhibited the greatest elasticity and resistance to deformation. Within the diol solvents (PEG 400, pentane 1,5-diol, propane 1,2-diol, propane 1,3-diol, and ethylene glycol), PEG 400 polyologels possessed the greatest elasticity and resistance to deformation, suggesting the importance of distance of separation between the diol groups. Using Raman spectroscopy bond formation between the polymer carbonyl group and the diol hydroxyl groups was observed. Polyologel mucoadhesion was influenced by viscoelasticity; maximum mucoadhesion was shown by glycerol polyologels at the highest polymer concentration (20% w/w). Similarly, the choice of solvent and concentration of PVM/MA affected the release of tetracycline from the polyologels. The controlled release of tetracycline for at least 10 h was observed for several polyologels, which, in combination with their excellent mucoadhesion and flow properties, offer possibilities for the clinical use of these systems to treat diseases within the oral cavity.
Keywords: Raman spectroscopy; drug release; flow rheology; mucoadhesion; oscillatory analysis; polyologel.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
An examination of the rheological and mucoadhesive properties of poly(acrylic acid) organogels designed as platforms for local drug delivery to the oral cavity.J Pharm Sci. 2007 Oct;96(10):2632-46. doi: 10.1002/jps.20771. J Pharm Sci. 2007. PMID: 17702045
-
Statistical modelling of the rheological and mucoadhesive properties of aqueous poly(methylvinylether-co-maleic acid) networks: Redefining biomedical applications and the relationship between viscoelasticity and mucoadhesion.Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2016 Aug 1;144:125-134. doi: 10.1016/j.colsurfb.2016.03.008. Epub 2016 Mar 4. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2016. PMID: 27085044
-
Rheological, mechanical and mucoadhesive properties of thermoresponsive, bioadhesive binary mixtures composed of poloxamer 407 and carbopol 974P designed as platforms for implantable drug delivery systems for use in the oral cavity.Int J Pharm. 2009 May 8;372(1-2):49-58. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpharm.2009.01.006. Epub 2009 Jan 18. Int J Pharm. 2009. PMID: 19429268
-
Mucoadhesive polymeric platform for drug delivery; a comprehensive review.Curr Drug Deliv. 2015;12(2):139-56. doi: 10.2174/1567201811666140924124722. Curr Drug Deliv. 2015. PMID: 25911164 Review.
-
Drug delivery from the oral cavity: a focus on mucoadhesive buccal drug delivery systems.PDA J Pharm Sci Technol. 2012 Sep-Oct;66(5):466-500. doi: 10.5731/pdajpst.2012.00877. PDA J Pharm Sci Technol. 2012. PMID: 23035030 Review.
Cited by
-
Spectroscopic and Thermal Characterisation of Interpenetrating Hydrogel Networks (IHNs) Based on Polymethacrylates and Pluronics, and Their Physicochemical Stability under Aqueous Conditions.Polymers (Basel). 2024 Oct 1;16(19):2796. doi: 10.3390/polym16192796. Polymers (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39408506 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Sahoo S., Kumar N., Bhattacharya C., Sagiri S.S., Jain K., Pal K., Ray S.S., Nayak B. Organogels: Properties and applications in drug delivery. Des. Monomers Polym. 2011;14:95–108. doi: 10.1163/138577211X555721. - DOI
-
- Rocha J.C.B., Lopes J.D., Mascarenhas M.C.N., Arellano D.B., Guerreiro L.M.R., da Cunha R.L. Thermal and rheological properties of organogels formed by sugarcane or candelilla wax in soybean oil. Food Res. Int. 2013;50:318–323. doi: 10.1016/j.foodres.2012.10.043. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

