Electrospun PCL Filtration Membranes Enhanced with an Electrosprayed Lignin Coating to Control Wettability and Anti-Bacterial Properties
- PMID: 38475357
- PMCID: PMC10934707
- DOI: 10.3390/polym16050674
Electrospun PCL Filtration Membranes Enhanced with an Electrosprayed Lignin Coating to Control Wettability and Anti-Bacterial Properties
Abstract
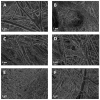
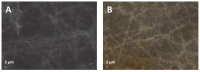
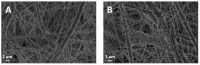
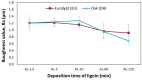
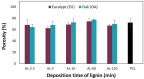
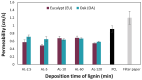
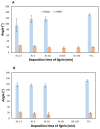
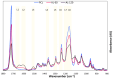
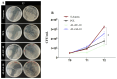
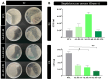
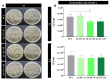
This study reports on the two-step manufacturing process of a filtration media obtained by first electrospinning a layer of polycaprolactone (PCL) non-woven fibers onto a paper filter backing and subsequently coating it by electrospraying with a second layer made of pure acidolysis lignin. The manufacturing of pure lignin coatings by solution electrospraying represents a novel development that requires fine control of the underlying electrodynamic processing. The effect of increasing deposition time on the lignin coating was investigated for electrospray time from 2.5 min to 120 min. Microstructural and physical characterization included SEM, surface roughness analysis, porosity tests, permeability tests by a Gurley densometer, ATR-FTIR analysis, and contact angle measurements vs. both water and oil. The results indicate that, from a functional viewpoint, such a natural coating endowed the membrane with an amphiphilic behavior that enabled modulating the nature of the bare PCL non-woven substrate. Accordingly, the intrinsic hydrophobic behavior of bare PCL electrospun fibers could be reduced, with a marked decrease already for a thin coating of less than 50 nm. Instead, the wettability of PCL vs. apolar liquids was altered in a less predictable manner, i.e., producing an initial increase of the oil contact angles (OCA) for thin lignin coating, followed by a steady decrease in OCA for higher densities of deposited lignin. To highlight the effect of the lignin type on the results, two grades of oak (AL-OA) of the Quercus cerris L. species and eucalyptus (AL-EU) of the Eucalyptus camaldulensis Dehnh species were compared throughout the investigation. All grades of lignin yielded coatings with measurable antibacterial properties, which were investigated against Staphylococcus aureus and Escherichia coli, yielding superior results for AL-EU. Remarkably, the lignin coatings did not change overall porosity but smoothed the surface roughness and allowed modulating air permeability, which is relevant for filtration applications. The findings are relevant for applications of this abundant biopolymer not only for filtration but also in biotechnology, health, packaging, and circular economy applications in general, where the reuse of such natural byproducts also brings a fundamental demanufacturing advantage.
Keywords: FTIR; PCL; SEM; antibacterial test; electrospinning; electrospraying; eucalyptus; lignin; morphology; oak; wettability.
Conflict of interest statement
Authors Noemi Fiaschini and Luis Alexander Hein were employed by the company NANOFABER S.r.l. These authors declare that NANOFABER S.r.l. contributed to the methodology and to the manufacturing of the prototype materials on its premises in the scope of the referenced EU projects NEWSKIN and I4GREEN. Author Marco Brecciaroli was employed by the company Simitecno srl, which did not take part in the conceptualization and provided roughness analysis in-kind and free-of-charge. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results. All authors took the decision to submit the manuscript and conducted the research in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest. In particular, this work does not represent work for hire, paid advertisement, or work for profit because it was supported by public funding from H2020 projects by the EC.
Figures

References
-
- Pendergast M.M., Hoek E.M. A review of water treatment membrane nanotechnologies. Energy Environ. Sci. 2011;4:1946–1971. doi: 10.1039/c0ee00541j. - DOI
-
- Abd Halim N.S., Wirzal M.D.H., Bilad M.R., Md Nordin N.A.H., Adi Putra Z., Sambudi N.S., Mohd Yusoff A.R. Improving performance of electrospun nylon 6, 6 nanofiber membrane for produced water filtration via solvent vapor treatment. Polymers. 2019;11:2117. doi: 10.3390/polym11122117. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Cui J., Lu T., Li F., Wang Y., Lei J., Ma W., Zou Y., Huang C. Flexible and transparent composite nanofibre membrane that was fabricated via a “green” electrospinning method for efficient particulate matter 2.5 capture. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2021;582:506–514. doi: 10.1016/j.jcis.2020.08.075. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

