Genome-Wide Analysis of Aux/IAA Gene Family in Artemisia argyi: Identification, Phylogenetic Analysis, and Determination of Response to Various Phytohormones
- PMID: 38475411
- PMCID: PMC10934841
- DOI: 10.3390/plants13050564
Genome-Wide Analysis of Aux/IAA Gene Family in Artemisia argyi: Identification, Phylogenetic Analysis, and Determination of Response to Various Phytohormones
Abstract
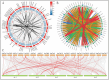
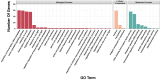
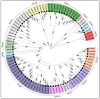
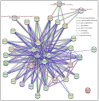
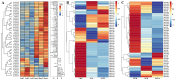
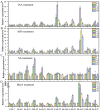
Artemisia argyi is a traditional herbal medicine plant, and its folium artemisia argyi is widely in demand due to moxibustion applications globally. The Auxin/indole-3-acetic acid (Aux/IAA, or IAA) gene family has critical roles in the primary auxin-response process, with extensive involvement in plant development and stresses, controlling various essential traits of plants. However, the systematic investigation of the Aux/IAA gene family in A. argyi remains limited. In this study, a total of 61 Aux/IAA genes were comprehensively identified and characterized. Gene structural analysis indicated that 46 Aux/IAA proteins contain the four typical domains, and 15 Aux/IAA proteins belong to non-canonical IAA proteins. Collinear prediction and phylogenetic relationship analyses suggested that Aux/IAA proteins were grouped into 13 distinct categories, and most Aux/IAA genes might experience gene loss during the tandem duplication process. Promoter cis-element investigation indicated that Aux/IAA promoters contain a variety of plant hormone response and stress response cis-elements. Protein interaction prediction analysis demonstrated that AaIAA26/29/7/34 proteins are possibly core members of the Aux/IAA family interaction. Expression analysis in roots and leaves via RNA-seq data indicated that the expression of some AaIAAs exhibited tissue-specific expression patterns, and some AaIAAs were involved in the regulation of salt and saline-alkali stresses. In addition, RT-qPCR results indicated that AaIAA genes have differential responses to auxin, with complex response patterns in response to other hormones, indicating that Aux/IAA may play a role in connecting auxin and other hormone signaling pathways. Overall, these findings shed more light on AaIAA genes and offer critical foundational knowledge toward the elucidation of their function during plant growth, stress response, and hormone networking of Aux/IAA family genes in A. argyi.
Keywords: Artemisia argyi; Aux/IAA family; expression pattern; function prediction.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Liu Y., He Y.A., Wang F., Xu R.C., Yang M., Ci Z.M., Wu Z.F., Zhang D.K., Lin J.Z. From longevity grass to contemporary soft gold: Explore the chemical constituents, pharmacology, and toxicology of Artemisia argyi H.Lev. & vaniot essential oil. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2021;279:114404. - PubMed
-
- Wang W., Zhang X.-K., Wu N., Fu Y.-J., Zu Y.-G. Antimicrobial activities of essential oil from Artemisiae argyi leaves. J. For. Res. 2006;17:332–334. doi: 10.1007/s11676-006-0077-2. - DOI
-
- Jiang Z., Guo X., Zhang K., Sekaran G., Cao B., Zhao Q., Zhang S., Kirby G.M., Zhang X. The Essential Oils and Eucalyptol from Artemisia vulgaris L. Prevent Acetaminophen-Induced Liver Injury by Activating Nrf2–Keap1 and Enhancing APAP Clearance through Non-Toxic Metabolic Pathway. Front. Pharmacol. 2019;10:782. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2019.00782. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
- 22A360012/Key Scientific Research Project of Higher Education Institutions in Henan Province
- No.14 [2018]/Chinese herbal medicine industry technology system of Henan Province
- 82204551/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 2060302/Key project at central government level: The ability establishment of sustainable use for valuable Chinese medicine resources
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

