Genetic Diversity Analysis and Core Germplasm Construction of Rubus chingii Hu
- PMID: 38475465
- PMCID: PMC10934504
- DOI: 10.3390/plants13050618
Genetic Diversity Analysis and Core Germplasm Construction of Rubus chingii Hu
Abstract
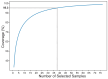
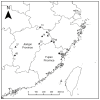
Rubus chingii Hu is the only species that is used for both edible and medicinal purposes among the 194 species of the genus Rubus in China. It is well known for its sweet and sour fresh fruits that are rich in vitamins and for its dried immature fruits that are used to treat kidney-related ailments. This study aims to evaluate genetic diversity and population structure and build a core germplasm repository of 132 R. chingii accessions from the provinces of Jiangxi and Fujian, using Hyper-seq-derived single-nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) markers. This is the first genetic study of R. chingii based on SNP molecular markers, and a total of 1,303,850 SNPs and 433,159 insertions/deletions (InDels) were identified. Low values for observed heterozygosity, nucleotide diversity (Pi) and fixation indexes (Fis) indicated low genetic diversity within populations, and an analysis of molecular variance (AMOVA) showed that 37.4% and 62.6% of the variations were found between populations and within samples, respectively. Four main clusters were identified by means of neighbor-joining (NJ) trees, the ADMIXTURE program and principal component analysis (PCA). Based on the genetic diversity, we finally constructed 38 representative core collections, representing 50% of the total core germplasm samples and 95.3% of the genotypes. In summary, the results of our study can provide valuable information on the genetic structure of R. chingii germplasm resources, which is helpful for further explorations of potential high-quality genes and for formulating future breeding and conservation strategies.
Keywords: Rubus chingii Hu; SNP; core collection; genetic diversity; population structure.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Yin Y., Jing Z., Zhang K., Liu X., Li S., Liu H. Study on Ecological Suitability Regionalization of Rubus chingii. Mod. Chin. Med. 2019;21:1342–1347. doi: 10.13313/j.issn.1673-4890.20190512001. (In Chinese) - DOI
-
- Editorial Committee of Flora of China, Chinese Academy of Sciences . Flora of China. Volume 37. Science Press; Beijing, China: 1990. p. 118.
-
- Jin L., Li C., Zhan S., Li X., Hua J. Chromosome count and estimation of genome size of Rubus chingii Hu. Mol. Plant Breed. 2022;20:6009–6014. (In Chinese)
-
- Guan Y., Qu B., Wang H., Chen L., Li H., Guo X., Liu J., Liu H., Zhang R. Research progress of Raspberry and its mature fruit. Chin. Arch. Tradit. Chin. Med. 2023;41:1–5. doi: 10.13193/j.issn.1673-7717.2023.01.001. (In Chinese) - DOI
Grants and funding
- 20224BAB215002/Jiangxi Provincial Natural Science Foundation of China
- 20212BCJ25024/Jiangxi Provincial Introduced Intelligence Program
- 20212BCJ25025/Jiangxi Provincial Introduced Intelligence Program
- S2023KJHZH0040/Jiangxi Provincial International Science and Technology Cooperation Program
- 000000/Jiujiang City "double hundred double thousand" talent project
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

