Distributing Plant Developmental Regulatory Proteins via Plasmodesmata
- PMID: 38475529
- PMCID: PMC10933835
- DOI: 10.3390/plants13050684
Distributing Plant Developmental Regulatory Proteins via Plasmodesmata
Abstract
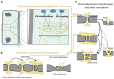
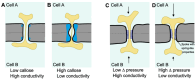
During plant development, mobile proteins, including transcription factors, abundantly serve as messengers between cells to activate transcriptional signaling cascades in distal tissues. These proteins travel from cell to cell via nanoscopic tunnels in the cell wall known as plasmodesmata. Cellular control over this intercellular movement can occur at two likely interdependent levels. It involves regulation at the level of plasmodesmata density and structure as well as at the level of the cargo proteins that traverse these tunnels. In this review, we cover the dynamics of plasmodesmata formation and structure in a developmental context together with recent insights into the mechanisms that may control these aspects. Furthermore, we explore the processes involved in cargo-specific mechanisms that control the transport of proteins via plasmodesmata. Instead of a one-fits-all mechanism, a pluriform repertoire of mechanisms is encountered that controls the intercellular transport of proteins via plasmodesmata to control plant development.
Keywords: KNOTTED1; SHORTROOT; intercellular communication; non-cell-autonomous transcription factors; plant meristem; plasmodesmata.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Symplastic intercellular transport from a developmental perspective.J Exp Bot. 2014 Apr;65(7):1857-63. doi: 10.1093/jxb/eru067. Epub 2014 Mar 11. J Exp Bot. 2014. PMID: 24619998 Review.
-
Symplastic communication in organ formation and tissue patterning.Curr Opin Plant Biol. 2016 Feb;29:21-8. doi: 10.1016/j.pbi.2015.10.007. Epub 2015 Dec 4. Curr Opin Plant Biol. 2016. PMID: 26658335 Review.
-
Plasmodesmata: intercellular tunnels facilitating transport of macromolecules in plants.Cell Tissue Res. 2013 Apr;352(1):49-58. doi: 10.1007/s00441-012-1550-1. Epub 2013 Feb 1. Cell Tissue Res. 2013. PMID: 23370600 Review.
-
Plasmodesmata: gatekeepers for cell-to-cell transport of developmental signals in plants.Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. 2000;16:393-421. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cellbio.16.1.393. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. 2000. PMID: 11031242 Review.
-
Emerging models on the regulation of intercellular transport by plasmodesmata-associated callose.J Exp Bot. 2017 Dec 18;69(1):105-115. doi: 10.1093/jxb/erx337. J Exp Bot. 2017. PMID: 29040641 Review.
Cited by
-
Plasmodesmata dynamics in bryophyte model organisms: secondary formation and developmental modifications of structure and function.Planta. 2024 Jul 4;260(2):45. doi: 10.1007/s00425-024-04476-1. Planta. 2024. PMID: 38965075 Free PMC article.
-
One organ to infect them all: the Cuscuta haustorium.Ann Bot. 2025 May 9;135(5):823-840. doi: 10.1093/aob/mcae208. Ann Bot. 2025. PMID: 39673400 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Virus-Free Micro-Corm Induction and the Mechanism of Corm Development in Taro.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Apr 16;26(8):3740. doi: 10.3390/ijms26083740. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40332369 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanisms of plant virus cell-to-cell transport: new lessons from complementation studies.Front Plant Sci. 2024 Sep 18;15:1453464. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2024.1453464. eCollection 2024. Front Plant Sci. 2024. PMID: 39359631 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

