Action of GABAB receptor on local network oscillation in somatosensory cortex of oral part: focusing on NMDA receptor
- PMID: 38475711
- PMCID: PMC10935845
- DOI: 10.1186/s12576-024-00911-w
Action of GABAB receptor on local network oscillation in somatosensory cortex of oral part: focusing on NMDA receptor
Abstract
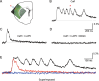
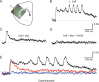
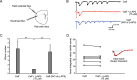
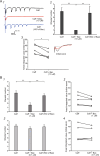
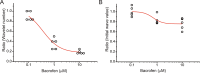
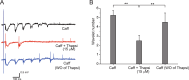
The balance of activity between glutamatergic and GABAergic networks is particularly important for oscillatory neural activities in the brain. Here, we investigated the roles of GABAB receptors in network oscillation in the oral somatosensory cortex (OSC), focusing on NMDA receptors. Neural oscillation at the frequency of 8-10 Hz was elicited in rat brain slices after caffeine application. Oscillations comprised a non-NMDA receptor-dependent initial phase and a later NMDA receptor-dependent oscillatory phase, with the oscillator located in the upper layer of the OSC. Baclofen was applied to investigate the actions of GABAB receptors. The later NMDA receptor-dependent oscillatory phase completely disappeared, but the initial phase did not. These results suggest that GABAB receptors mainly act on NMDA receptor, in which metabotropic actions of GABAB receptors may contribute to the attenuation of NMDA receptor activities. A regulatory system for network oscillation involving GABAB receptors may be present in the OSC.
Keywords: Caffeine; GABAB receptor; NMDA receptor; Network oscillation; Oral somatosensory cortex; Voltage-sensitive dye.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclose.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Interplay between non-NMDA and NMDA receptor activation during oscillatory wave propagation: Analyses of caffeine-induced oscillations in the visual cortex of rats.Neural Netw. 2016 Jul;79:141-9. doi: 10.1016/j.neunet.2016.03.012. Epub 2016 Apr 8. Neural Netw. 2016. PMID: 27136667
-
Multiple tooth-losses during development suppress age-dependent emergence of oscillatory neural activities in the oral somatosensory cortex.Brain Res. 2008 Aug 11;1224:37-42. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2008.06.002. Epub 2008 Jun 10. Brain Res. 2008. PMID: 18573238
-
NMDA receptor-dependent GABAB receptor internalization via CaMKII phosphorylation of serine 867 in GABAB1.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010 Aug 3;107(31):13924-9. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1000909107. Epub 2010 Jul 19. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010. PMID: 20643921 Free PMC article.
-
The roles of GABAB receptors in cortical network activity.Adv Pharmacol. 2010;58:205-29. doi: 10.1016/S1054-3589(10)58009-8. Adv Pharmacol. 2010. PMID: 20655484 Review.
-
GABAB receptor trafficking and interacting proteins: targets for the development of highly specific therapeutic strategies to treat neurological disorders?Biochem Pharmacol. 2013 Dec 1;86(11):1525-30. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2013.09.016. Epub 2013 Sep 29. Biochem Pharmacol. 2013. PMID: 24084431 Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

