De novo assembly and annotation of Popillia japonica's genome with initial clues to its potential as an invasive pest
- PMID: 38475721
- PMCID: PMC10936072
- DOI: 10.1186/s12864-024-10180-x
De novo assembly and annotation of Popillia japonica's genome with initial clues to its potential as an invasive pest
Abstract
Background: The spread of Popillia japonica in non-native areas (USA, Canada, the Azores islands, Italy and Switzerland) poses a significant threat to agriculture and horticulture, as well as to endemic floral biodiversity, entailing that appropriate control measures must be taken to reduce its density and limit its further spread. In this context, the availability of a high quality genomic sequence for the species is liable to foster basic research on the ecology and evolution of the species, as well as on possible biotechnologically-oriented and genetically-informed control measures.
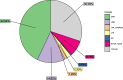
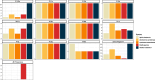
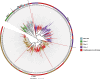
Results: The genomic sequence presented and described here is an improvement with respect to the available draft sequence in terms of completeness and contiguity, and includes structural and functional annotations. A comparative analysis of gene families of interest, related to the species ecology and potential for polyphagy and adaptability, revealed a contraction of gustatory receptor genes and a paralogous expansion of some subgroups/subfamilies of odorant receptors, ionotropic receptors and cytochrome P450s.
Conclusions: The new genomic sequence as well as the comparative analyses data may provide a clue to explain the staggering invasive potential of the species and may serve to identify targets for potential biotechnological applications aimed at its control.
Keywords: Beetles; Cytochrome P450; Gustatory receptors; Invasive species; Ionotropic receptors; Japanese beetle; Odorant receptors.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures




Similar articles
-
A high-quality de novo genome assembly based on nanopore sequencing of a wild-caught coconut rhinoceros beetle (Oryctes rhinoceros).BMC Genomics. 2022 Jun 7;23(1):426. doi: 10.1186/s12864-022-08628-z. BMC Genomics. 2022. PMID: 35672676 Free PMC article.
-
The direction, timing and demography of Popillia japonica (Coleoptera) invasion reconstructed using complete mitochondrial genomes.Sci Rep. 2024 Mar 26;14(1):7120. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-57667-x. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38531924 Free PMC article.
-
Genomic content of chemosensory genes correlates with host range in wood-boring beetles (Dendroctonus ponderosae, Agrilus planipennis, and Anoplophora glabripennis).BMC Genomics. 2019 Sep 2;20(1):690. doi: 10.1186/s12864-019-6054-x. BMC Genomics. 2019. PMID: 31477011 Free PMC article.
-
A nationwide pest risk analysis in the context of the ongoing Japanese beetle invasion in Continental Europe: The case of metropolitan France.Front Insect Sci. 2022 Dec 12;2:1079756. doi: 10.3389/finsc.2022.1079756. eCollection 2022. Front Insect Sci. 2022. PMID: 38468800 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Beetle genomes in the 21st century: prospects, progress and priorities.Curr Opin Insect Sci. 2018 Feb;25:76-82. doi: 10.1016/j.cois.2017.12.002. Epub 2017 Dec 18. Curr Opin Insect Sci. 2018. PMID: 29602365 Review.
Cited by
-
Characterization of chemosensory genes in the subterranean pest Gryllotalpa Orientalis based on genome assembly and transcriptome comparison.BMC Genomics. 2025 Jan 14;26(1):33. doi: 10.1186/s12864-025-11217-5. BMC Genomics. 2025. PMID: 39810101 Free PMC article.
-
Chromosome-level genome of the shining chafers Kibakoganea tamdaoensis (Coleoptera: Scarabaeidae: Rutelinae).Sci Data. 2025 Aug 1;12(1):1345. doi: 10.1038/s41597-025-05657-7. Sci Data. 2025. PMID: 40751049 Free PMC article.
-
Whole Genome Resequencing Reveals Origins and Global Invasion Pathways of the Japanese Beetle Popillia japonica.Mol Ecol. 2025 Aug;34(16):e70008. doi: 10.1111/mec.70008. Epub 2025 Jul 2. Mol Ecol. 2025. PMID: 40600371 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Fleming WE. Biology of the Japanese beetle. Tech bull. 1976;1449:1–129.
-
- Althoff ER, Rice KB. Japanese Beetle (Coleoptera: Scarabaeidae) Invasion of North America: History, Ecology, and Management. J Integr Pest Manag. 2022;13:2. doi: 10.1093/jipm/pmab043. - DOI
-
- Strangi A, Paoli F, Nardi F, Shimizu K, Kimoto T, Iovinella I, et al. Tracing the dispersal route of the invasive Japanese beetle Popillia japonica. J Pest Sci. 2023 doi: 10.1007/s10340-023-01653-1. - DOI
-
- Lessio F, Pisa CG, Picciau L, Ciampitti M, Cavagna B, Alma A. An immunomarking method to investigate the flight distance of the Japanese beetle. Entomol Gen. 2022;42:45–56.
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

