Assessing the research landscape and clinical utility of large language models: a scoping review
- PMID: 38475802
- PMCID: PMC10936025
- DOI: 10.1186/s12911-024-02459-6
Assessing the research landscape and clinical utility of large language models: a scoping review
Abstract
Importance: Large language models (LLMs) like OpenAI's ChatGPT are powerful generative systems that rapidly synthesize natural language responses. Research on LLMs has revealed their potential and pitfalls, especially in clinical settings. However, the evolving landscape of LLM research in medicine has left several gaps regarding their evaluation, application, and evidence base.
Objective: This scoping review aims to (1) summarize current research evidence on the accuracy and efficacy of LLMs in medical applications, (2) discuss the ethical, legal, logistical, and socioeconomic implications of LLM use in clinical settings, (3) explore barriers and facilitators to LLM implementation in healthcare, (4) propose a standardized evaluation framework for assessing LLMs' clinical utility, and (5) identify evidence gaps and propose future research directions for LLMs in clinical applications.
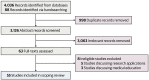
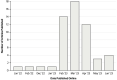
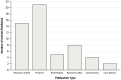
Evidence review: We screened 4,036 records from MEDLINE, EMBASE, CINAHL, medRxiv, bioRxiv, and arXiv from January 2023 (inception of the search) to June 26, 2023 for English-language papers and analyzed findings from 55 worldwide studies. Quality of evidence was reported based on the Oxford Centre for Evidence-based Medicine recommendations.
Findings: Our results demonstrate that LLMs show promise in compiling patient notes, assisting patients in navigating the healthcare system, and to some extent, supporting clinical decision-making when combined with human oversight. However, their utilization is limited by biases in training data that may harm patients, the generation of inaccurate but convincing information, and ethical, legal, socioeconomic, and privacy concerns. We also identified a lack of standardized methods for evaluating LLMs' effectiveness and feasibility.
Conclusions and relevance: This review thus highlights potential future directions and questions to address these limitations and to further explore LLMs' potential in enhancing healthcare delivery.
Question What is the current state of Large Language Models’ (LLMs) application in clinical settings, and what are the primary challenges and opportunities associated with their integration? Findings This scoping review, analyzing 55 studies, indicates that while LLMs, including OpenAI’s ChatGPT, show potential in compiling patient notes, aiding in healthcare navigation, and supporting clinical decision-making, their use is constrained by data biases, the generation of plausible but incorrect information, and various ethical and privacy concerns. A significant variability in the rigor of studies, especially in evaluating LLM responses, calls for standardized evaluation methods, including established metrics like ROUGE, METEOR, G-Eval, and MultiMedQA. Meaning The findings suggest a need for enhanced methodologies in LLM research, stressing the importance of integrating real patient data and considering social determinants of health, to improve the applicability and safety of LLMs in clinical environments.
Keywords: ChatGPT; Clinical settings; Large language models; Natural language processing; Scoping review.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- OpenAI. Introducing ChatGPT [Internet]. [cited 2023 May 2]. Available from: https://openai.com/blog/chatgpt.
-
- Devlin J, Chang MW, Lee K, Toutanova K, BERT. Pre-training of deep bidirectional Transformers for language understanding [Internet]. arXiv. 2018. Available from: https://arxiv.org/abs/1810.04805.
-
- Levine DM, Tuwani R, Kompa B, Varma A, Finlayson SG, Mehrotra A et al. The Diagnostic and Triage Accuracy of the GPT-3 Artificial Intelligence Model [Internet]. medRxiv. 2023. 10.1101/2023.01.30.23285067. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources