Endothelial-specific telomerase inactivation causes telomere-independent cell senescence and multi-organ dysfunction characteristic of aging
- PMID: 38475941
- PMCID: PMC11296101
- DOI: 10.1111/acel.14138
Endothelial-specific telomerase inactivation causes telomere-independent cell senescence and multi-organ dysfunction characteristic of aging
Abstract
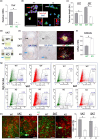
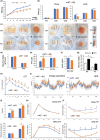
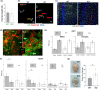
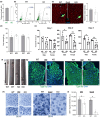
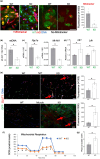
It has remained unclear how aging of endothelial cells (EC) contributes to pathophysiology of individual organs. Cell senescence results in part from inactivation of telomerase (TERT). Here, we analyzed mice with Tert knockout specifically in EC. Tert loss in EC induced transcriptional changes indicative of senescence and tissue hypoxia in EC and in other cells. We demonstrate that EC-Tert-KO mice have leaky blood vessels. The blood-brain barrier of EC-Tert-KO mice is compromised, and their cognitive function is impaired. EC-Tert-KO mice display reduced muscle endurance and decreased expression of enzymes responsible for oxidative metabolism. Our data indicate that Tert-KO EC have reduced mitochondrial content and function, which results in increased dependence on glycolysis. Consistent with this, EC-Tert-KO mice have metabolism changes indicative of increased glucose utilization. In EC-Tert-KO mice, expedited telomere attrition is observed for EC of adipose tissue (AT), while brain and skeletal muscle EC have normal telomere length but still display features of senescence. Our data indicate that the loss of Tert causes EC senescence in part through a telomere length-independent mechanism undermining mitochondrial function. We conclude that EC-Tert-KO mice is a model of expedited vascular senescence recapitulating the hallmarks aging, which can be useful for developing revitalization therapies.
Keywords: accelerated aging; endothelial; hypoxia; knockout; metabolism; mitochondrial disease; senescence; telomerase.
© 2024 The Authors. Aging Cell published by Anatomical Society and John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Ait‐Aissa, K. , Norwood‐Toro, L. E. , Terwoord, J. , Young, M. , Paniagua, L. A. , Hader, S. N. , Hughes, W. E. , Hockenberry, J. C. , Beare, J. E. , Linn, J. , Kohmoto, T. , Kim, J. , Betts, D. H. , LeBlanc, A. J. , Gutterman, D. D. , & Beyer, A. M. (2022). Noncanonical role of telomerase in regulation of microvascular redox environment with implications for coronary artery disease. Function, 3, zqac043. 10.1093/function/zqac043 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Ale‐Agha, N. , Jakobs, P. , Goy, C. , Zurek, M. , Rosen, J. , Dyballa‐Rukes, N. , Metzger, S. , Greulich, J. , von Ameln, F. , Eckermann, O. , Unfried, K. , Brack, F. , Grandoch, M. , Thielmann, M. , Kamler, M. , Gedik, N. , Kleinbongard, P. , Heinen, A. , Heusch, G. , … Haendeler, J. (2021). Mitochondrial telomerase reverse transcriptase protects from myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury by improving complex I composition and function. Circulation, 144, 1876–1890. 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.120.051923 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Assmus, B. , Urbich, C. , Aicher, A. , Hofmann, W. K. , Haendeler, J. , Rossig, L. , Spyridopoulos, I. , Zeiher, A. M. , & Dimmeler, S. (2003). HMG‐CoA reductase inhibitors reduce senescence and increase proliferation of endothelial progenitor cells via regulation of cell cycle regulatory genes. Circulation Research, 92, 1049–1055. 10.1161/01.RES.0000070067.64040.7C - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

