The Anatomic and Functional Outcomes of Ozurdex-Aided Vitrectomy in Proliferative Diabetic Retinopathy
- PMID: 38476345
- PMCID: PMC10929653
- DOI: 10.2147/DMSO.S445607
The Anatomic and Functional Outcomes of Ozurdex-Aided Vitrectomy in Proliferative Diabetic Retinopathy
Abstract
Purpose: To investigate the 3-months outcomes of patients who underwent intraoperative intravitreal injection of Ozurdex for proliferative diabetic retinopathy (PDR).
Methods: This is a prospective randomized controlled clinical trial (ChiCTR2100043399). Seventy-one patients with PDR who had indications for surgery without intravitreal injection history within 3 months preoperatively were enrolled. Patients were randomly divided into three groups based on the medicine injected intraoperatively: Ozurdex, Conbercept, and Control group. The primary outcome is the best-corrected visual acuity (BCVA) within 3 months postoperatively. The secondary outcomes include the intraocular pressure (IOP), mean sensitivity, central retinal thickness and vessels perfusion.
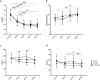
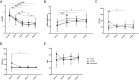
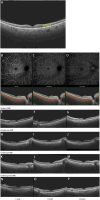
Results: The BCVA and the mean sensitivity improved in the three groups (F = 130.8, P < 0.0001; F = 34.18, P < 0.0001), but there was no statistical difference among the three groups (F = 0.858, P = 0.552; F = 0.964, P = 0.452). The IOP was no significant differences among the three groups within 3 months postoperatively (F = 0.881, P = 0.533). Compared with the other two groups, central retinal thickness (CRT) and outer retinal layer (ORL) thickness decreased significantly in patients of the Ozurdex group (F = 3.037, P = 0.008; F = 2.626, P = 0.018), especially in the diabetic macular edema (DME) patients (F = 2.761, P = 0.0164; F = 2.572, P = 0.0240). In macular region, superficial vascular plexus (SVP), intermediate capillary plexus (ICP) and deep capillary plexus (DCP) perfusion were not shown statistical difference at 3 months postoperatively in the all three groups compared with 1 day postoperatively (P > 0.05).
Conclusion: Compared with the other two groups, anatomical outcomes was improved significantly in Ozurdex group for DR patients. Ozurdex may help to improve the visual acuity and visual sensitivity, and there is no significant difference in the change of IOP and microvascular improvement.
Clinical trial registration: This trial is registered with the Chinese Clinical Trial Registry (http://www.chictr.org.cn, registration number ChiCTR2100043399).
Keywords: microperimetry; optical coherence tomography angiography; ozurdex; pars plana vitrectomy; proliferative diabetic retinopathy.
© 2024 Wang et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures

Similar articles
-
ASSOCIATION OF MACULAR STRUCTURE WITH MICROPERIMETRY SENSITIVITY FOLLOWING VITRECTOMY FOR PROLIFERATE DIABETIC RETINOPATHY.Retina. 2024 Jun 1;44(6):982-990. doi: 10.1097/IAE.0000000000004063. Retina. 2024. PMID: 38767849
-
Microvascular Changes After Conbercept Intravitreal Injection of PDR With or Without Center-Involved Diabetic Macular Edema Analyzed by OCTA.Front Med (Lausanne). 2022 Mar 22;9:797087. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2022.797087. eCollection 2022. Front Med (Lausanne). 2022. PMID: 35391880 Free PMC article.
-
The effect of adjunctive intravitreal conbercept at the end of diabetic vitrectomy for the prevention of post-vitrectomy hemorrhage in patients with severe proliferative diabetic retinopathy: a prospective, randomized pilot study.BMC Ophthalmol. 2020 Feb 3;20(1):43. doi: 10.1186/s12886-020-1321-9. BMC Ophthalmol. 2020. PMID: 32013913 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Practical Lessons from Protocol I for the Management of Diabetic Macular Edema.Dev Ophthalmol. 2017;60:91-108. doi: 10.1159/000459692. Epub 2017 Apr 20. Dev Ophthalmol. 2017. PMID: 28427069 Review.
-
Intravitreal steroids for macular edema in diabetes.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 Nov 17;11(11):CD005656. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD005656.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020. PMID: 33206392 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Enhancing the outcomes of diabetic vitrectomy with pharmacological adjuvants.World J Methodol. 2025 Jun 20;15(2):98912. doi: 10.5662/wjm.v15.i2.98912. eCollection 2025 Jun 20. World J Methodol. 2025. PMID: 40548210 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

