Investigation of the miRNA-mRNA Regulatory Circuits and Immune Signatures Associated with Bronchopulmonary Dysplasia
- PMID: 38476468
- PMCID: PMC10929271
- DOI: 10.2147/JIR.S448394
Investigation of the miRNA-mRNA Regulatory Circuits and Immune Signatures Associated with Bronchopulmonary Dysplasia
Abstract
Background: Bronchopulmonary dysplasia (BPD) has become a major cause of morbidity and mortality in preterm infants worldwide, yet its pathogenesis and underlying mechanisms remain poorly understood. The present study sought to explore microRNA-mRNA regulatory networks and immune cells involvement in BPD through a combination of bioinformatic analysis and experimental validation.
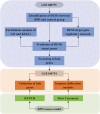
Methods: MicroRNA and mRNA microarray datasets were obtained from the Gene Expression Omnibus (GEO) database. Differentially expressed microRNAs (DEMs) were identified in BPD patients compared to control subjects, and their target genes were predicted using miRWalk, miRNet, miRDB, and TargetScan databases. Subsequently, protein-protein interaction (PPI) and functional enrichment analyses were conducted on the target genes. 30 hub genes were screened using the Cytohubba plugin of the Cytoscape software. Additionally, mRNA microarray data was utilized to validate the expression of hub genes and to perform immune infiltration analysis. Finally, real-time PCR (RT-PCR), immunohistochemistry (IHC), and flow cytometry were conducted using a mouse model of BPD to confirm the bioinformatics findings.
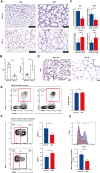
Results: Two DEMs (miR-15b-5p and miR-20a-5p) targeting genes primarily involved in the regulation of cell cycle phase transition, ubiquitin ligase complex, protein serine/threonine kinase activity, and MAPK signaling pathway were identified. APP and four autophagy-related genes (DLC1, PARP1, NLRC4, and NRG1) were differentially expressed in the mRNA microarray dataset. Analysis of immune infiltration revealed significant differences in levels of neutrophils and naive B cells between BPD patients and control subjects. RT-PCR and IHC confirmed reduced expression of APP in a mouse model of BPD. Although the proportion of total neutrophils did not change appreciably, the activation of neutrophils, marked by loss of CD62L, was significantly increased in BPD mice.
Conclusion: Downregulation of APP mediated by miR-15b-5p and miR-20a-5p may be associated with the development of BPD. Additionally, increased CD62L- neutrophil subset might be important for the immune-mediated injury in BPD.
Keywords: CD62L− neutrophil; bronchopulmonary dysplasia; immune infiltration analysis; miRNA-mRNA regulatory circuits.
© 2024 Li et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Comprehensive analysis of miRNA-mRNA regulatory network and potential drugs in chronic chagasic cardiomyopathy across human and mouse.BMC Med Genomics. 2021 Nov 29;14(1):283. doi: 10.1186/s12920-021-01134-3. BMC Med Genomics. 2021. PMID: 34844599 Free PMC article.
-
Integrative analysis of lncRNAs, miRNAs, and mRNAs-associated ceRNA network in a neonatal mouse model of bronchopulmonary dysplasia.J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med. 2021 Oct;34(19):3234-3245. doi: 10.1080/14767058.2020.1815700. Epub 2020 Sep 13. J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med. 2021. PMID: 32924699
-
[Expression of microRNA-495-5p in preterm infants with bronchopulmonary dysplasia: a bioinformatics analysis].Zhongguo Dang Dai Er Ke Za Zhi. 2020 Jan;22(1):24-30. doi: 10.7499/j.issn.1008-8830.2020.01.006. Zhongguo Dang Dai Er Ke Za Zhi. 2020. PMID: 31948520 Free PMC article. Chinese.
-
miR-3202 inhibits bronchopulmonary dysplasia-mediated apoptosis and oxidative stress in bronchial epithelial cells via targeting RAG1.Pathol Res Pract. 2024 Sep;261:155482. doi: 10.1016/j.prp.2024.155482. Epub 2024 Jul 23. Pathol Res Pract. 2024. PMID: 39067173
-
Using biological information to analyze potential miRNA-mRNA regulatory networks in the plasma of patients with non-small cell lung cancer.BMC Cancer. 2022 Mar 21;22(1):299. doi: 10.1186/s12885-022-09281-1. BMC Cancer. 2022. PMID: 35313857 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Analysis and validation of necroptosis-related diagnostic biomarkers associated with immune infiltration in bronchopulmonary dysplasia.Front Pediatr. 2025 Jul 15;13:1578628. doi: 10.3389/fped.2025.1578628. eCollection 2025. Front Pediatr. 2025. PMID: 40735606 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

