Data driven analysis reveals prognostic genes and immunological targets in human sepsis-associated acute kidney injury
- PMID: 38476535
- PMCID: PMC10925525
- DOI: 10.5847/wjem.j.1920-8642.2024.026
Data driven analysis reveals prognostic genes and immunological targets in human sepsis-associated acute kidney injury
Abstract
Background: The molecular mechanism of sepsis-associated acute kidney injury (SA-AKI) is unclear. We analyzed co-differentially expressed genes (co-DEGs) to elucidate the underlying mechanism and intervention targets of SA-AKI.
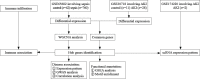
Methods: The microarray datasets GSE65682, GSE30718, and GSE174220 were downloaded from the Gene Expression Omnibus (GEO) database. We identified the co-DEGs and constructed a gene co-expression network to screen the hub genes. We analyzed immune correlations and disease correlations and performed functional annotation of the hub genes. We also performed single-cell and microenvironment analyses and investigated the enrichment pathways and the main transcription factors. Finally, we conducted a correlation analysis to evaluate the role of the hub genes.
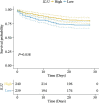
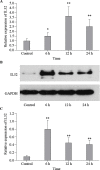
Results: Interleukin 32 (IL32) was identified as the hub gene in SA-AKI, and the main enriched signaling pathways were associated with hemopoiesis, cellular response to cytokine stimulus, inflammatory response, and regulation of kidney development. Additionally, IL32 was significantly associated with mortality in SA-AKI patients. Monocytes, macrophages, T cells, and NK cells were closely related to IL32 and were involved in the immune microenvironment in SA-AKI patients. IL32 expression increased significantly in the kidney of septic mouse. Toll-like receptor 2 (TLR2) was significantly and negatively correlated with IL32.
Conclusion: IL32 is the key gene involved in SA-AKI and is significantly associated with prognosis. TLR2 and relevant immune cells are closely related to key genes.
Keywords: Acute kidney injury; Bioinformatics analysis; Interleukin 32; Sepsis; Toll-like receptor 2.
Copyright: © World Journal of Emergency Medicine.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of interest: The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Uchino S, Kellum JA, Bellomo R, Doig GS, Morimatsu H, Morgera S, et al. Acute renal failure in critically ill patients:a multinational, multicenter study. JAMA. 2005;294(7):813–8. - PubMed
-
- Fani F, Regolisti G, Delsante M, Cantaluppi V, Castellano G, Gesualdo L, et al. Recent advances in the pathogenetic mechanisms of sepsis-associated acute kidney injury. J Nephrol. 2018;31(3):351–9. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
