Retrolaminar block for opioid-free anaesthesia and enhanced recovery after posterior lumbar discectomy: A randomised controlled study
- PMID: 38476544
- PMCID: PMC10926343
- DOI: 10.4103/ija.ija_773_23
Retrolaminar block for opioid-free anaesthesia and enhanced recovery after posterior lumbar discectomy: A randomised controlled study
Abstract
Background and aims: Intraoperative regional analgesia and enhanced recovery are standard care models aimed at reducing perioperative opioid use following spine surgeries. This study aimed to examine the analgesic effect of retrolaminar block in promoting recovery and pain relief after posterior lumbar discectomy.
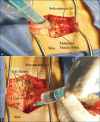
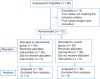
Methods: The patients undergoing elective posterior lumbar discectomy were randomised into the retrolaminar group (n = 36) (received an intra-operative bilateral retrolaminar block with 15 mL of bupivacaine 0.25%, 2 mL (8 mg) of dexamethasone, and 2 mL of magnesium sulphate 10% (200 mg) on each side) and control group (n = 36) (received standard general anaesthesia). Primary outcomes were recovery time (time from isoflurane discontinuation to the first response to verbal command) and time to discharge (time from admission to the post-anaesthesia care unit (PACU) to discharge from the PACU, when Aldrete score was ≥9). P values < 0.05 were considered statistically significant.
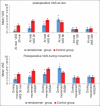
Results: The extubation, recovery, and discharge times were significantly shorter in the retrolaminar group compared to the control group (P < 0.001). Postoperative pain scores were significantly lower in the retrolaminar group for up to 8 h compared to only 2 h in the control group (P < 0.001). The time to first administration of ketorolac post-operatively was significantly longer in the retrolaminar group compared to the control group (P < 0.001). The total consumption of ketorolac post-operatively was significantly reduced in the retrolaminar group compared to the control group (P < 0.001).
Conclusion: Intra-operative retrolaminar block is an easy and effective opioid-free regional anaesthesia technique that improves recovery after posterior lumbar discectomy.
Keywords: Discectomy; enhanced recovery after surgery; nerve block; opioid; opioid-free anaesthesia; regional anaesthesia; retrolaminar block.
Copyright: © 2024 Indian Journal of Anaesthesia.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
