Royal Jelly, A Super Food, Protects Against Celecoxib-Induced Renal Toxicity in Adult Male Albino Rats
- PMID: 38476622
- PMCID: PMC10929035
- DOI: 10.1177/20543581241235526
Royal Jelly, A Super Food, Protects Against Celecoxib-Induced Renal Toxicity in Adult Male Albino Rats
Abstract
Background: Celecoxib is a COX-2 nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID). It is widely used for the treatment of osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, and ankylosing spondylitis.
Objective: This study aimed to explore the effect of long-term administration of celecoxib on kidney of male albino rats, and to study the potential effect of treatment discontinuation on such tissues. The study also examined the alleged ameliorative effect of royal jelly (RJ).
Methods: Fifty, male albino rats were divided into 5 equal groups; 10 each. Group 1: rats received no drug (control group). Group 2: rats received celecoxib (50 mg/kg/day, orally for 30 successive days). Group 3: rats received celecoxib (50 mg/kg/day, orally) and royal jelly (300 mg/kg/day, orally) for 30 successive days. Group 4: rats received celecoxib for 30 successive days, then rats were left untreated for another 30 days. Group 5: rats received celecoxib and RJ for 30 successive days, then rats were left untreated for another 30 days.
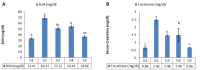
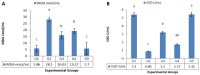
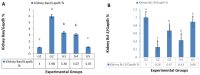
Results: Long-term celecoxib administration caused significant elevation in kidney function tests, with ameliorative effects of RJ against celecoxib-induced renal toxicity.
Conclusion: Long-term celecoxib administration caused renal toxicity in male albino rats, with ameliorative effects of RJ.
Contexte: Le célécoxib est un anti-inflammatoire non stéroïdien (AINS) inhibiteur de COX-2. Ce médicament est largement utilisé pour le traitement symptomatique de l’arthrose, de la polyarthrite rhumatoïde et de la spondylarthrite ankylosante.
Objectifs: Cet essai visait à examiner l’effet d’une administration à long terme de célécoxib sur les reins de rats albinos mâles, à étudier les possibles effets de l’arrêt du traitement sur ces tissus et à vérifier l’effet d’amélioration allégué de la gelée royale.
Méthodologie: Cinquante rats albinos mâles ont été répartis en cinq groupes égaux (10 rats par groupe). Groupe 1 (groupe témoin): rats n’ayant reçu aucun médicament. Groupe 2: rats ayant reçu du célécoxib (50 mg/kg/jour, par voie orale pendant 30 jours consécutifs). Groupe 3: rats ayant reçu du célécoxib (50 mg/kg/jour, par voie orale) et de la gelée royale (300 mg/kg/jour, par voie orale) pendant 30 jours consécutifs. Groupe 4: rats ayant reçu du célécoxib pendant 30 jours consécutifs, puis laissés sans traitement pendant 30 jours supplémentaires. Groupe 5: rats ayant reçu du célécoxib et de la gelée royale pendant 30 jours consécutifs, puis laissés sans traitement pendant 30 jours supplémentaires.
Résultats: L’administration à long terme de célécoxib a entraîné une augmentation significative des tests de la fonction rénale; la gelée royale a montré des effets d’amélioration contre la toxicité rénale induite par le célécoxib.
Conclusion: L’administration à long terme de célécoxib a provoqué une toxicité rénale chez les rats albinos mâles contre laquelle la gelée royale a montré des effets protecteurs.
Keywords: celecoxib; kidney; renal; royal jelly; toxicity.
© The Author(s) 2024.
Conflict of interest statement
The author(s) declared no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Research progress on rat model of drug-induced liver injury established by nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (celecoxib) and royal jelly ameliorative effect.J Complement Integr Med. 2024 Jan 29;21(2):239-247. doi: 10.1515/jcim-2023-0385. eCollection 2024 Jun 1. J Complement Integr Med. 2024. PMID: 38281144
-
Cardioprotective role of royal jelly in the prevention of celecoxib-mediated cardiotoxicity in adult male albino rats.J Cardiothorac Surg. 2024 Mar 18;19(1):135. doi: 10.1186/s13019-024-02593-2. J Cardiothorac Surg. 2024. PMID: 38500210 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of gastric tolerability for long-term use of diclofenac and celecoxib in male albino rats and potential gastroprotective benefits of royal jelly: a randomized controlled trial.J Complement Integr Med. 2024 Dec 17;22(1):181-192. doi: 10.1515/jcim-2024-0324. eCollection 2025 Mar 1. J Complement Integr Med. 2024. PMID: 39680822 Clinical Trial.
-
Celecoxib: a review of its use for symptomatic relief in the treatment of osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis and ankylosing spondylitis.Drugs. 2011 Dec 24;71(18):2457-89. doi: 10.2165/11208240-000000000-00000. Drugs. 2011. PMID: 22141388 Review.
-
Renal safety and tolerability of celecoxib, a novel cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitor.Am J Ther. 2000 May;7(3):159-75. doi: 10.1097/00045391-200007030-00004. Am J Ther. 2000. PMID: 11317165 Review.
Cited by
-
Royal Jelly: Biological Action and Health Benefits.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 May 30;25(11):6023. doi: 10.3390/ijms25116023. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38892209 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Royal jelly alleviates gemcitabine-induced ovarian toxicity: an investigation on rat models.BMC Complement Med Ther. 2025 Jul 14;25(1):264. doi: 10.1186/s12906-025-05013-7. BMC Complement Med Ther. 2025. PMID: 40660206 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Clemett D, Goa KL. Celecoxib: a review of its use in osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis and acute pain. Drugs. 2000;59(4):957-980. - PubMed
-
- McCormack PL. Celecoxib: a review of its use for symptomatic relief in the treatment of osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis and ankylosing spondylitis. Drugs. 2011;71:2457-2489. - PubMed
-
- Whelton A, Maurath CJ, Verburg KM, Geis GS. Renal safety and tolerability of celecoxib, a novel cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitor. Am J Ther. 2000;7(3):159-175. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

