Molecular mechanism of endophytic bacteria DX120E regulating polyamine metabolism and promoting plant growth in sugarcane
- PMID: 38476689
- PMCID: PMC10927768
- DOI: 10.3389/fpls.2024.1334907
Molecular mechanism of endophytic bacteria DX120E regulating polyamine metabolism and promoting plant growth in sugarcane
Abstract
Introduction: Sugarcane endophytic nitrogen-fixing bacterium Klebsiella variícola DX120E displayed broad impact on growth, but the exact biological mechanism, especially polyamines (PAs) role, is still meager.
Methods: To reveal this relationship, the content of polyamine oxidase (PAO), PAs, reactive oxygen species (ROS)-scavenging antioxidative enzymes, phytohormones, 1-aminocyclopropane-1-carboxylic synthase (ACS), chlorophyll content, and biomass were determined in sugarcane incubated with the DX120E strain. In addition, expression levels of the genes associated with polyamine metabolism were measured by transcriptomic analysis.
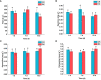
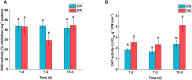
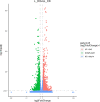
Results: Genomic analysis of Klebsiella variícola DX120E revealed that 39 genes were involved in polyamine metabolism, transport, and the strain secrete PAs in vitro. Following a 7-day inoculation period, DX120E stimulated an increase in the polyamine oxidase (PAO) enzyme in sugarcane leaves, however, the overall PAs content was reduced. At 15 days, the levels of PAs, ROS-scavenging antioxidative enzymes, and phytohormones showed an upward trend, especially spermidine (Spd), putrescine (Put), catalase (CAT), auxin (IAA), gibberellin (GA), and ACS showed a significant up-regulation. The GO and KEGG enrichment analysis found a total of 73 differentially expressed genes, involving in the cell wall (9), stimulus response (13), peroxidase activity (33), hormone (14) and polyamine metabolism (4).
Discussion: This study demonstrated that endophytic nitrogen-fixing bacteria stimulated polyamine metabolism and phytohormones production in sugarcane plant tissues, resulting in enhanced growth. Dual RNA-seq analyses provided insight into the early-stage interaction between sugarcane seedlings and endophytic bacteria at the transcriptional level. It showed how diverse metabolic processes selectively use distinct molecules to complete the cell functions under present circumstances.
Keywords: Klebsiella; antioxidative; interaction; phytohormone; transcriptomic.
Copyright © 2024 Qin, Khan, Yan, Wang, Pan, Huang, Wei, Guo, Li, Dong and Xing.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures







Similar articles
-
Endophytic nitrogen-fixing bacteria DX120E inoculation altered the carbon and nitrogen metabolism in sugarcane.Front Microbiol. 2022 Nov 7;13:1000033. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.1000033. eCollection 2022. Front Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 36419423 Free PMC article.
-
Complete genome sequence of endophytic nitrogen-fixing Klebsiella variicola strain DX120E.Stand Genomic Sci. 2015 May 8;10:22. doi: 10.1186/s40793-015-0004-2. eCollection 2015. Stand Genomic Sci. 2015. PMID: 26203334 Free PMC article.
-
[Growth-promoting effect of inoculating Klebsiella variicola DX120E on different sugarcane cultivars].Ying Yong Sheng Tai Xue Bao. 2014 Jul;25(7):2085-92. Ying Yong Sheng Tai Xue Bao. 2014. PMID: 25345062 Chinese.
-
Polyamine Oxidase-Generated Reactive Oxygen Species in Plant Development and Adaptation: The Polyamine Oxidase-NADPH Oxidase Nexus.Antioxidants (Basel). 2022 Dec 17;11(12):2488. doi: 10.3390/antiox11122488. Antioxidants (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36552696 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Polyamine metabolism in different pathological states of the brain.Mol Chem Neuropathol. 1992 Jun;16(3):241-71. doi: 10.1007/BF03159973. Mol Chem Neuropathol. 1992. PMID: 1358085 Review.
Cited by
-
Genome-driven insights into Bacillus safensis strain B7 as a seed coating agent for plant growth promotion and alleviation of biotic and abiotic stresses.PLoS One. 2025 Aug 18;20(8):e0329619. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0329619. eCollection 2025. PLoS One. 2025. PMID: 40824923 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Agisha V. N., Eapen S. J., Monica V., Sheoran N., Munjal V., Suseelabhai R., et al. . (2017). Plant endophytic Pseudomonas putida BP25 induces expression of defense genes in black pepper roots: Deciphering through suppression subtractive hybridization analysis. Physiol. Mol. Plant P. 100, 106–116. doi: 10.1016/j.pmpp.2017.07.006 - DOI
-
- Asghari S., Harighi B., Ashengroph M., Clement C., Aziz A., Esmaeel Q., et al. . (2020). Induction of systemic resistance to Agrobacterium tumefaciens by endophytic bacteria in grapevine. Plant Pathol. 69, 827–837. doi: 10.1111/ppa.13175 - DOI
-
- Bahari Saravi H., Gholami A., Pirdashti H., Baradaran Firouzabadi M., Asghari H., Yaghoubian Y. (2022). Improvement of salt tolerance in Stevia rebaudiana by co-application of endophytic fungi and exogenous spermidine. Ind. Crops Prod. 177, 114443. doi: 10.1016/j.indcrop.2021.114443 - DOI
-
- Carolina K. K., Felipe I., d. S. F., Eny I. S. F., Marcos P. M. A., Heloiza R. B. (2018). Sugarcane growth promotion by Kosakonia sp. ICB117 an endophytic and diazotrophic bacterium. Afr. J. Microbiol. Res. 12, 105–114. doi: 10.5897/AJMR2017.8738 - DOI
-
- Chen T., White J. F., Li C., Nan Z. (2021). Exogenous spermidine enhances Epichloe endophyte-induced tolerance to NaCl stress in wild barley (Hordeum brevisubulatum). Plant Soil. 468, 77–95. doi: 10.1007/s11104-021-05109-2 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

