Novel underlying genetic markers for asthenozoospermia due to abnormal spermatogenesis and reproductive organ inflammation
- PMID: 38476923
- PMCID: PMC10928817
- DOI: 10.3892/etm.2024.12434
Novel underlying genetic markers for asthenozoospermia due to abnormal spermatogenesis and reproductive organ inflammation
Abstract
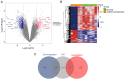
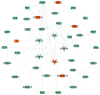
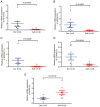
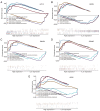
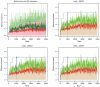
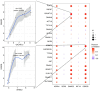
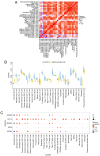
Asthenozoospermia, a male fertility disorder, has a complex and multifactorial etiology. Moreover, the effectiveness of different treatments for asthenozoospermia remains uncertain. Hence, by using bioinformatics techniques, the present study aimed to determine the underlying genetic markers and pathogenetic mechanisms associated with asthenozoospermia due to abnormal spermatogenesis and inflammation of the reproductive tract. GSE160749 dataset was downloaded from the Gene Expression Omnibus database, and the data were filtered to obtain 1336 differentially expressed genes (DEGs) associated with asthenozoospermia. These DEGs were intersected with the epithelial mesenchymal transition datasets to yield 61 candidate DEGs. Gene Ontology and Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes pathway enrichment analyses were performed, and the results revealed that these candidate DEGs were significantly enriched in the enzyme-linked receptor pathway and the thyroid hormone pathway. A protein-protein interaction network was constructed to identify the key genes of asthenozoospermia. A total of five key genes were identified, among which SOX9 was significantly upregulated, while HSPA4, SMAD2, HIF1A and GSK3B were significantly downregulated. These findings were validated by conducting reverse transcription-quantitative PCR for clinical semen samples. To determine the underlying molecular mechanisms, a regulatory network of transcription factors and miRNA-mRNA interactions was predicted. The expression levels of HSPA4, SMAD2 and GSK3B were positively associated with several related etiological genes of asthenozoospermia. In total, five key genes were closely associated with the level and type of immune cells; higher levels of activated B cells and CD8 T cells were observed in asthenozoospermia. Thus, the findings of the present study may provide clues to determine the underlying novel diagnostic genetic markers and treatment strategies for asthenozoospermia.
Keywords: asthenozoospermia; bioinformatics techniques; genetic markers; immune cells; reproductive organ inflammation; spermatogenesis.
Copyright: © 2024 Zhang et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Bioinformatics analysis identifies potential hub genes and crucial pathways in the pathogenesis of asthenozoospermia.BMC Med Genomics. 2022 Dec 5;15(1):252. doi: 10.1186/s12920-022-01407-5. BMC Med Genomics. 2022. PMID: 36471356 Free PMC article.
-
RNA-sequencing and bioinformatics analysis of long noncoding RNAs and mRNAs in the asthenozoospermia.Biosci Rep. 2020 Jul 31;40(7):BSR20194041. doi: 10.1042/BSR20194041. Biosci Rep. 2020. PMID: 32614449 Free PMC article.
-
Screening, identification and interaction analysis of key MicroRNAs and genes in Asthenozoospermia.Int J Med Sci. 2021 Feb 6;18(7):1670-1679. doi: 10.7150/ijms.54460. eCollection 2021. Int J Med Sci. 2021. PMID: 33746583 Free PMC article.
-
Key Genes Associated with Pyroptosis in Gout and Construction of a miRNA-mRNA Regulatory Network.Cells. 2022 Oct 17;11(20):3269. doi: 10.3390/cells11203269. Cells. 2022. PMID: 36291136 Free PMC article.
-
An in silico analysis of human sperm genes associated with asthenozoospermia and its implication in male infertility.Medicine (Baltimore). 2018 Dec;97(49):e13338. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000013338. Medicine (Baltimore). 2018. PMID: 30544396 Free PMC article.
References
-
- WHO-World Health Organization. WHO Laboratory Manual for the Examination and Processing of Human Semen (6th ed). In: Examination and post-examination procedures. WHO. 2021. https://apps.who.int/iris/rest/bitstreams/1358672/retrieve. Accessed 27 Jul, 2021.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
