Retrospective Analysis of Clinical Characteristics and Outcomes of Pregnant Women with SARS-CoV-2 Infections Admitted to Intensive Care Units in India (Preg-CoV): A Multicenter Study
- PMID: 38477010
- PMCID: PMC10926030
- DOI: 10.5005/jp-journals-10071-24656
Retrospective Analysis of Clinical Characteristics and Outcomes of Pregnant Women with SARS-CoV-2 Infections Admitted to Intensive Care Units in India (Preg-CoV): A Multicenter Study
Abstract
Aim: The aim was to examine the outcomes of pregnant women admitted to intensive care unit with coronavirus disease-2019 (COVID-19) infection during the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) pandemic in India. The primary outcome of the study was maternal mortality at day 30. The secondary outcomes were the intensive care unit (ICU) and hospital length of stay, fetal mortality and preterm delivery.
Materials and methods: This was a retrospective multicentric cohort study. Ethical clearance was obtained. All pregnant women of the 15-45-year age admitted to ICUs with SARS-CoV-2 infection during 1st March 2020 to 31st October, 2021 were included.
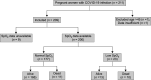
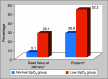
Results: Data were collected from nine centers and for 211 obstetric patients admitted to the ICU with a confirmed diagnosis of COVID-19. They were divided in to two groups as per their SpO2 (saturation of peripheral oxygen) level at admission on room air, that is, normal SpO2 group (SpO2 > 90%) and low SpO2 group (SpO2 < 90%). The mean age was (30.06 ± 4.25) years and the gestational age was 36 ± 8 weeks. The maternal mortality rate was10.53%. The rate of fetal death and preterm delivery was 7.17 and 28.22%, respectively. The average ICU and hospital length of stay (LOS) were 6.35 ± 8.56 and 6.78 ± 6.04 days, respectively. The maternal mortality (6.21 vs 43.48%, p < 0.001), preterm delivery (26.55 vs 52.17%, p = 0.011) and fetal death (5.08 vs 26.09%, p = 0.003) were significantly higher in the low SpO2 group.
Conclusion: The overall maternal mortality among critically ill pregnant women affected with COVID-19 infection was 10.53%. The rate of preterm birth and fetal death were 28.22 and 7.17%, respectively. These adverse maternal and fetal outcomes were significantly higher in those admitted with low SpO2 (<90%) at admission compared with those with normal SpO2.
How to cite this article: Sinha S, Paul G, Shah BA, Karmata T, Paliwal N, Dobariya J, et al. Retrospective Analysis of Clinical Characteristics and Outcomes of Pregnant Women with SARS-CoV-2 Infections Admitted to Intensive Care Units in India (Preg-CoV): A Multicenter Study. Indian J Crit Care Med 2024;28(3):265-272.
Keywords: Coronavirus disease-2019; Intensive care unit; Maternal mortality; Obstetric critical care; Pregnant women.
Copyright © 2024; The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Source of support: Funding and technological support was received from Indian Society of Critical Care Medicine (ISCCM). Conflict of interest: None
Figures

References
-
- Villar J, Arif S, Gunier RB, Thiruvengadam R, Rauch S, Kholin A, et al. Maternal and neonatal morbidity and mortality among pregnant women with and without COVID-19 infection: The INTERCOVID multinational cohort study. JAMA Pediatr. 2021;175(8):817–826. doi: 10.1001/jamapediatrics.2021.1050. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- DeBolt CA, Bianco A, Limaye MA, Silverstein J, Penfeld CA, Roman AS, et al. Pregnant women with severe or critical coronavirus disease 2019 have increased composite morbidity compared with nonpregnant matched controls. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2021;224(5):510.e1–510.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.ajog.2020.11.022. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
