Analysing and quantifying chronic stress-associated endogenous steroids in hair samples
- PMID: 38477213
- PMCID: PMC11635064
- DOI: 10.1002/dta.3678
Analysing and quantifying chronic stress-associated endogenous steroids in hair samples
Abstract
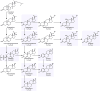
In previous studies, various steroids have been associated with stress and have therefore been quantified to investigate stress-related questions. Since the main stress-related steroid cortisol follows a circadian rhythm, often hair is analysed to quantify this steroid. Further, hair analysis gives the unique possibility of long-time monitoring by analysing a certain segment of hair, since hair grows on average 1 cm per month. Hair is a difficult matrix due to the complex sample preparation with many steps including washing and grinding, followed by various extraction steps. Additionally, steroids are endogenous and are therefore present in the hair matrix. Hence, no analyte free matrix is available, which is needed for the quantification via external calibrators. To overcome this problem, the so-called surrogate methods can be used, for which a 13C3 labelled or deuterated reference compound of the steroid of interest is used for quantification. In the present study, a surrogate method was developed and fully validated for the quantitative analysis of seven steroids in human hair. Validation experiments showed that the method is further suitable for semi-quantitative analysis of estradiol. However, it is not suitable for the analysis of androsterone and DHEAS. The method was successfully used to analyse steroids in a comprehensive study of 360 adolescent hair samples, enabling research into stress markers.
Keywords: LC–MS/MS; cortisol; hair analysis; steroids; stress.
© 2024 The Authors. Drug Testing and Analysis published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interest or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures


References
-
- Stubsjøen SM, Bohlin J, Dahl E, et al. Assessment of chronic stress in sheep (part I): the use of cortisol and cortisone in hair as non‐invasive biological markers. Small Rumin Res. 2015;132:25‐31. doi:10.1016/j.smallrumres.2015.09.015 - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

