Nanowire Array Breath Acetone Sensor for Diabetes Monitoring
- PMID: 38477429
- PMCID: PMC11109654
- DOI: 10.1002/advs.202309481
Nanowire Array Breath Acetone Sensor for Diabetes Monitoring
Abstract
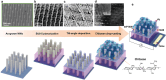
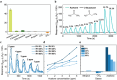
Diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA) is a life-threatening acute complication of diabetes characterized by the accumulation of ketone bodies in the blood. Breath acetone, a ketone, directly correlates with blood ketones. Therefore, monitoring breath acetone can significantly enhance the safety and efficacy of diabetes care. In this work, the design and fabrication of an InP/Pt/chitosan nanowire array-based chemiresistive acetone sensor is reported. By incorporation of chitosan as a surface-functional layer and a Pt Schottky contact for efficient charge transfer processes and photovoltaic effect, self-powered, highly selective acetone sensing is achieved. The sensor has exhibited an ultra-wide acetone detection range from sub-ppb to >100 000 ppm level at room temperature, covering those in the exhaled breath from healthy individuals (300-800 ppb) to people at high risk of DKA (>75 ppm). The nanowire sensor has also been successfully integrated into a handheld breath testing prototype, the Ketowhistle, which can successfully detect different ranges of acetone concentrations in simulated breath samples. The Ketowhistle demonstrates the immediate potential for non-invasive ketone monitoring for people living with diabetes, in particular for DKA prevention.
Keywords: Diabetic ketoacidosis; InP nanowires; acetone sensor; breath test prototype; chitosan.
© 2024 The Authors. Advanced Science published by Wiley‐VCH GmbH.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have filed a provisional patent for this work.
Figures



References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- FutureFellowshipgrant(FT200100939)/Australian Research Council
- Discoverygrant(DP190101864)/Australian Research Council
- NS210100083/National Intelligence and Security Discovery Research
- Our Health in Our Hands (OHIOH)/Australian National University
- a strategic initiative/Australian National University
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
