A nomogram based on TFE3 IHC results and clinical factors as a preliminary screening scheme for TFE3-rearranged renal cell carcinoma
- PMID: 38477529
- PMCID: PMC10935875
- DOI: 10.1002/cam4.6813
A nomogram based on TFE3 IHC results and clinical factors as a preliminary screening scheme for TFE3-rearranged renal cell carcinoma
Abstract
Background: TFE3 immunohistochemistry (TFE3-IHC) is controversial in the diagnosis of TFE3-rearranged renal cell carcinoma (TFE3-rearranged RCC). This study is to investigate the accuracy and sensitivity of IHC and establish a predictive model to diagnose TFE3-rearranged RCC.
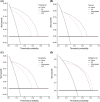
Methods: Retrospective analysis was performed by collecting IHC and fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH) results from 228 patients. IHC results were evaluated using three scoring systems. Scoring system 1 is graded based on nuclear staining intensity, scoring system 2 is graded based on the percentage of stained tumor cell nuclei, and scoring system 3 is graded based on both the nuclear staining intensity and the percentage. We collected patients' IHC results and clinical information. Important variables were screened based on univariate logistic regression analysis. Then, independent risk factors were established through multivariate logistic regression, and a nomogram model was constructed. The model was validated in internal test set and external validation set. The receiver operating characteristic curve (ROC curve), calibration curve, and decision curve analysis (DCA) were generated to assess discriminative ability of the model.
Results: The accuracy of IHC based on three scoring systems were 0.829, 0.772, and 0.807, respectively. The model included four factors including age, gender, lymph node metastasis and IHC results. Area under the curve (AUC) values were 0.935 for the training set, 0.934 for the internal test set, 0.933 for all 228 patients, and 0.916 for the external validation set.
Conclusions: TFE3 IHC has high accuracy in the diagnosis of TFE3-rearranged RCC. Clinical information such as age and lymph node metastasis are independent risk factors, which can be used as a supplement to the results of TFE3 IHC. This study confirms the value of IHC in the diagnosis of TFE3-rearranged RCC. The accuracy of the diagnosis can be improved by incorporating IHC with other clinical risk factors.
Keywords: TFE3-rearranged renal cell carcinoma; diagnosis; fluorescence in situ hybridization; immunohistochemistry.
© 2023 The Authors. Cancer Medicine published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Sidhar SK, Clark J, Gill S, et al. The t(X;1)(p11.2;q21.2) translocation in papillary renal cell carcinoma fuses a novel gene PRCC to the TFE3 transcription factor gene. Hum Mol Genet. 1996;5(9):1333‐1338. - PubMed
-
- Humphrey PA, Moch H, Cubilla AL, Ulbright TM, Reuter VE. The 2016 WHO classification of tumours of the urinary system and male genital organs‐part B: prostate and bladder tumours. Eur Urol. 2016;70(1):106‐119. - PubMed
-
- Argani P. MiT family translocation renal cell carcinoma. Semin Diagn Pathol. 2015;32(2):103‐113. - PubMed
-
- Moch H, Amin MB, Berney DM, et al. The 2022 World Health Organization classification of tumours of the urinary system and male genital organs‐part a: renal, penile, and testicular tumours. Eur Urol. 2022;82(5):458‐468. - PubMed
-
- Sukov WR, Hodge JC, Lohse CM, et al. TFE3 rearrangements in adult renal cell carcinoma: clinical and pathologic features with outcome in a large series of consecutively treated patients. Am J Surg Pathol. 2012;36(5):663‐670. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 2017B020227004/Guangdong Provincial Science and Technology Foundation of China
- 2017A030313538/Guangdong Provincial Science and Technology Foundation of China
- 81725016/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 81872094/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 81772718/National Natural Science Foundation of China
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

