Elevated level of circulating calprotectin correlates with severity and high mortality in patients with COVID-19
- PMID: 38477671
- PMCID: PMC10936233
- DOI: 10.1002/iid3.1212
Elevated level of circulating calprotectin correlates with severity and high mortality in patients with COVID-19
Abstract
Background: Patients with coronavirus disease-2019 (COVID-19) are characterized by hyperinflammation. Calprotectin (S100A8/S100A9) is a calcium- and zinc-binding protein mainly secreted by neutrophilic granulocytes or macrophages and has been suggested to be correlated with the severity and prognosis of COVID-19.
Aim: To thoroughly evaluate the diagnostic and prognostic utility of calprotectin in patients with COVID-19 by analyzing relevant studies.
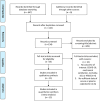
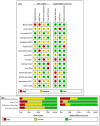
Methods: PubMed, Web of Science, and Cochrane Library were comprehensively searched from inception to August 1, 2023 to retrieve studies about the application of calprotectin in COVID-19. Useful data such as the level of calprotectin in different groups and the diagnostic efficacy of this biomarker for severe COVID-19 were extracted and aggregated by using Stata 16.0 software.
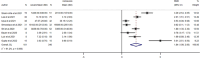
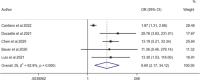
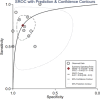
Results: Fifteen studies were brought into this meta-analysis. First, the pooled standardized mean differences (SMDs) were used to estimate the differences in the levels of circulating calprotectin between patients with severe and non-severe COVID-19. The results showed an overall estimate of 1.84 (95% confidence interval [CI]: 1.09-2.60). Diagnostic information was extracted from 11 studies, and the pooled sensitivity and specificity of calprotectin for diagnosing severe COVID-19 were 0.75 (95% CI: 0.64-0.84) and 0.88 (95% CI: 0.79-0.94), respectively. The AUC was 0.89 and the pooled DOR was 18.44 (95% CI: 9.07-37.51). Furthermore, there was a strong correlation between elevated levels of circulating calprotectin and a higher risk of mortality outcomes in COVID-19 patients (odds ratio: 8.60, 95% CI: 2.17-34.12; p < 0.1).
Conclusion: This meta-analysis showed that calprotectin was elevated in patients with severe COVID-19, and this atypical inflammatory cytokine might serve as a useful biomarker to distinguish the severity of COVID-19 and predict the prognosis.
Keywords: COVID-19; biomarker; calprotectin; meta-analysis; systematic review.
© 2024 The Authors. Immunity, Inflammation and Disease published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- WHO . Coronavirus Disease (COVID‐19) Dashboard. 2020. Accessed November 26, 2023. https://data.who.int/dashboards/covid19/deaths?n=c
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

