Immunogenicity and Safety of a Purified Vero Rabies Vaccine-Serum Free, Compared With 2 Licensed Vaccines, in a Simulated Rabies Post-Exposure Regimen in Healthy Adults in France: A Randomized, Controlled, Phase 3 Trial
- PMID: 38478634
- PMCID: PMC11175674
- DOI: 10.1093/cid/ciae137
Immunogenicity and Safety of a Purified Vero Rabies Vaccine-Serum Free, Compared With 2 Licensed Vaccines, in a Simulated Rabies Post-Exposure Regimen in Healthy Adults in France: A Randomized, Controlled, Phase 3 Trial
Erratum in
-
Correction to: Immunogenicity and Safety of a Purified Vero Rabies Vaccine-Serum Free, Compared With 2 Licensed Vaccines, in a Simulated Rabies Post-Exposure Regimen in Healthy Adults in France: A Randomized, Controlled, Phase 3 Trial.Clin Infect Dis. 2024 Oct 15;79(4):1124. doi: 10.1093/cid/ciae390. Clin Infect Dis. 2024. PMID: 39196975 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
Background: A next-generation Vero cell rabies vaccine (PVRV-NG2) was developed using the same Pitman-Moore strain as in the licensed purified Vero cell vaccine (PVRV; Verorab) and the human diploid cell vaccine (HDCV; Imovax Rabies®).
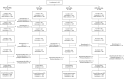
Methods: This dual-center, modified, double-blind, phase 3 study evaluated the immunogenic non-inferiority and safety of PVRV-NG2 with and without concomitant intramuscular human rabies immunoglobulin (HRIG) versus PVRV + HRIG and HDCV + HRIG in a simulated post-exposure prophylaxis (PEP) regimen. Healthy adults ≥18 years old (N = 640) were randomized 3:1:1:1 to PVRV-NG2 + HRIG, PVRV + HRIG, HDCV + HRIG, or PVRV-NG2 alone (administered as single vaccine injections on days [D] 0, D3, D7, D14, and 28, with HRIG on D0 in applicable groups). Rabies virus neutralizing antibodies (RVNA) titers were assessed pre- (D0) and post-vaccination (D14, D28, and D42) using the rapid fluorescent focus inhibition test. Non-inferiority, based on the proportion of participants achieving RVNA titers ≥0.5 IU/mL (primary objective), was demonstrated if the lower limit of the 95% CI of the difference in proportions between PVRV-NG2 + HRIG and PVRV + HRIG/HDCV + HRIG was >-5% at D28. Safety was assessed up to 6 months after the last injection.
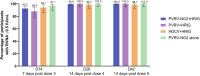
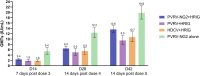
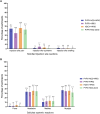
Results: Non-inferiority of PVRV-NG2 + HRIG compared with PVRV + HRIG and HDCV + HRIG was demonstrated. Nearly all participants (99.6%, PVRV-NG2 + HRIG; 100%, PVRV + HRIG; 98.7%, HDCV + HRIG; 100%, PVRV-NG2 alone) achieved RVNA titers ≥0.5 IU/mL at D28. Geometric mean titers were similar between groups with concomitant HRIG administration at all time points. Safety profiles were similar between PVRV-NG2 and comparator vaccines.
Conclusions: In a simulated PEP setting, PVRV-NG2 + HRIG showed comparable immunogenicity and safety to current standard-of-care vaccines.
Clinical trials registration: NCT03965962.
Keywords: PVRV-NG2; immunogenicity; post-exposure prophylaxis; rabies; safety.
© The Author(s) 2024. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of Infectious Diseases Society of America.
Conflict of interest statement
Potential conflicts of interest. A. C. P. P., Q. J., C. P., J. K. P., V. B., S. B., S. P., F. G. M., and A. M. M. are employees of Sanofi and may hold shares and/or stock options in the company. Y. D. reports other financial or nonfinancial interests as investigator and CEO of 1 of the investigation sites. All other authors report no potential conflicts. All authors have submitted the ICMJE Form for Disclosure of Potential Conflicts of Interest. Conflicts that the editors consider relevant to the content of the manuscript have been disclosed.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Safety and immunogenicity of a serum-free purified Vero rabies vaccine in comparison with the rabies human diploid cell vaccine (HDCV; Imovax® Rabies) administered in a simulated rabies post-exposure regimen in healthy adults.Vaccine. 2024 Apr 11;42(10):2553-2559. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2023.11.052. Epub 2023 Dec 16. Vaccine. 2024. PMID: 38105138
-
Non-inferiority study of purified Vero rabies vaccine - serum free in three-dose and two-dose pre-exposure prophylaxis regimens in comparison with licensed rabies vaccines.Clin Infect Dis. 2024 Nov 26:ciae581. doi: 10.1093/cid/ciae581. Online ahead of print. Clin Infect Dis. 2024. PMID: 39587931
-
Safety and immunogenicity of three dose levels of an investigational, highly purified Vero cell rabies vaccine: A randomized, controlled, observer-blinded, Phase II study with a simulated post-exposure regimen in healthy adults.Hum Vaccin Immunother. 2023 Dec 15;19(3):2275453. doi: 10.1080/21645515.2023.2275453. Epub 2023 Nov 3. Hum Vaccin Immunother. 2023. PMID: 37921410 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Immunogenicity and safety of human diploid cell vaccine (HDCV) vs. purified Vero cell vaccine (PVRV) vs. purified chick embryo cell vaccine (PCECV) used in post-exposure prophylaxis: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Hum Vaccin Immunother. 2022 Dec 31;18(1):2027714. doi: 10.1080/21645515.2022.2027714. Epub 2022 Feb 22. Hum Vaccin Immunother. 2022. PMID: 35192787 Free PMC article.
-
Post-exposure prophylaxis (PEP) for rabies with purified chick embryo cell vaccine: a systematic literature review and meta-analysis.Expert Rev Vaccines. 2018 Jun;17(6):525-545. doi: 10.1080/14760584.2018.1473765. Epub 2018 Jun 25. Expert Rev Vaccines. 2018. PMID: 29939085 Review.
Cited by
-
Randomized Controlled Trial of the Immunogenicity and Safety of a Serum-Free Purified Vero Rabies Vaccine (PVRV-NG2) Using a Simulated Postexposure Zagreb Regimen With Human Rabies Immunoglobulin in Adults in Thailand.Open Forum Infect Dis. 2024 Oct 25;11(11):ofae633. doi: 10.1093/ofid/ofae633. eCollection 2024 Nov. Open Forum Infect Dis. 2024. PMID: 39544495 Free PMC article.
-
Infection and Prevention of Rabies Viruses.Microorganisms. 2025 Feb 9;13(2):380. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms13020380. Microorganisms. 2025. PMID: 40005749 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- World Health Organization . Rabies epidemiology and burden. Available at: https://www.who.int/teams/control-of-neglected-tropical-diseases/rabies/.... Accessed 19 February 2024.
-
- World Health Organization . Rabies. Available at: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/rabies. Accessed January 2023.
-
- World Health Organization . Rabies vaccines: WHO position paper, April 2018–Recommendations. Vaccine.2018; 36(37):5500-5503. - PubMed
-
- Wang S-Y, Sun J-F, Liu P, et al. Immunogenicity and safety of human diploid cell vaccine (HDCV) vs. purified Vero cell vaccine (PVRV) vs. purified chick embryo cell vaccine (PCECV) used in post-exposure prophylaxis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Hum Vaccin Immunother 2022; 18:2027714. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

