A type I interferon regulatory network for human plasmacytoid dendritic cells based on heparin, membrane-bound and soluble BDCA-2
- PMID: 38478694
- PMCID: PMC10963015
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.2312404121
A type I interferon regulatory network for human plasmacytoid dendritic cells based on heparin, membrane-bound and soluble BDCA-2
Abstract
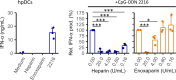
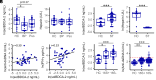
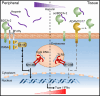
Plasmacytoid dendritic cells (pDCs) produce type I interferons (IFNs) after sensing viral/bacterial RNA or DNA by toll-like receptor (TLR) 7 or TLR9, respectively. However, aberrant pDCs activation can cause adverse effects on the host and contributes to the pathogenesis of type I IFN-related autoimmune diseases. Here, we show that heparin interacts with the human pDCs-specific blood dendritic cell antigen 2 (BDCA-2) but not with related lectins such as DCIR or dectin-2. Importantly, BDCA-2-heparin interaction depends on heparin sulfation and receptor glycosylation and results in inhibition of TLR9-driven type I IFN production in primary human pDCs and the pDC-like cell line CAL-1. This inhibition is mediated by unfractionated and low-molecular-weight heparin, as well as endogenous heparin from plasma, suggesting that the local blood environment controls the production of IFN-α in pDCs. Additionally, we identified an activation-dependent soluble form of BDCA-2 (solBDCA-2) in human plasma that functions as heparin antagonist and thereby increases TLR9-driven IFN-α production in pDCs. Of importance, solBDCA-2 levels in the serum were increased in patients with scrub typhus (an acute infectious disease caused by Orientia tsutsugamushi) compared to healthy control subjects and correlated with anti-dsDNA antibodies titers. In contrast, solBDCA-2 levels in plasma from patients with bullous pemphigoid or psoriasis were reduced. In summary, this work identifies a regulatory network consisting of heparin, membrane-bound and solBDCA-2 modulating TLR9-driven IFN-α production in pDCs. This insight into pDCs function and regulation may have implications for the treatment of pDCs-related autoimmune diseases.
Keywords: BDCA-2; glycosaminoglycans; heparin; plasmacytoid dendritic cells; type I interferons.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests statement:The authors declare no competing interest.
Figures

References
-
- Gilliet M., Cao W., Liu Y. J., Plasmacytoid dendritic cells: Sensing nucleic acids in viral infection and autoimmune diseases. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 8, 594–606 (2008). - PubMed
-
- Blomberg S., Eloranta M.-L., Magnusson M., Alm G. V., Rönnblom L., Expression of the markers BDCA-2 and BDCA-4 and production of interferon-α by plasmacytoid dendritic cells in systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum 48, 2524–2532 (2003). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

