Barley AGO4 proteins show overlapping functionality with distinct small RNA-binding properties in heterologous complementation
- PMID: 38480545
- PMCID: PMC10937801
- DOI: 10.1007/s00299-024-03177-z
Barley AGO4 proteins show overlapping functionality with distinct small RNA-binding properties in heterologous complementation
Abstract
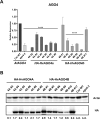
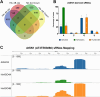
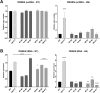
Barley AGO4 proteins complement expressional changes of epigenetically regulated genes in Arabidopsis ago4-3 mutant and show a distinct affinity for the 5' terminal nucleotide of small RNAs, demonstrating functional conservation and divergence. The function of Argonaute 4 (AGO4) in Arabidopsis thaliana has been extensively characterized; however, its role in monocots, which have large genomes abundantly supplemented with transposable elements (TEs), remains elusive. The study of barley AGO4 proteins can provide insights into the conserved aspects of RNA-directed DNA methylation (RdDM) and could also have further applications in the field of epigenetics or crop improvement. Bioinformatic analysis of RNA sequencing data identified two active AGO4 genes in barley, HvAGO4a and HvAGO4b. These genes function similar to AtAGO4 in an Arabidopsis heterologous complementation system, primarily binding to 24-nucleotide long small RNAs (sRNAs) and triggering methylation at specific target loci. Like AtAGO4, HvAGO4B exhibits a preference for binding sRNAs with 5' adenine residue, while also accepting 5' guanine, uracil, and cytosine residues. In contrast, HvAGO4A selectively binds only sRNAs with a 5' adenine residue. The diverse binding capacity of barley AGO4 proteins is reflected in TE-derived sRNAs and in their varying abundance. Both barley AGO4 proteins effectively restore the levels of extrachromosomal DNA and transcript abundancy of the heat-activated ONSEN retrotransposon to those observed in wild-type Arabidopsis plants. Our study provides insight into the distinct binding specificities and involvement in TE regulation of barley AGO4 proteins in Arabidopsis by heterologous complementation.
Keywords: Arabidopsis thaliana; Hordeum vulgare; ARGONAUTE 4 (AGO4); Heat stress; RNA-directed DNA methylation; Small RNAs; Transposable elements.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that may be perceived as influencing their work.
Figures



Similar articles
-
The mechanisms of siRNA selection by plant Argonaute proteins triggering DNA methylation.Nucleic Acids Res. 2022 Dec 9;50(22):12997-13010. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkac1135. Nucleic Acids Res. 2022. PMID: 36477368 Free PMC article.
-
Arabidopsis AGO3 predominantly recruits 24-nt small RNAs to regulate epigenetic silencing.Nat Plants. 2016 Apr 18;2(5):16049. doi: 10.1038/nplants.2016.49. Nat Plants. 2016. PMID: 27243648
-
Enzymatic reactions of AGO4 in RNA-directed DNA methylation: siRNA duplex loading, passenger strand elimination, target RNA slicing, and sliced target retention.Genes Dev. 2023 Feb 1;37(3-4):103-118. doi: 10.1101/gad.350240.122. Epub 2023 Feb 6. Genes Dev. 2023. PMID: 36746605 Free PMC article.
-
siRNA-mediated chromatin maintenance and its function in Arabidopsis thaliana.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2011 Aug;1809(8):444-51. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagrm.2011.05.002. Epub 2011 May 13. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2011. PMID: 21605714 Review.
-
Small regulatory RNAs in rice epigenetic regulation.Biochem Soc Trans. 2022 Jun 30;50(3):1215-1225. doi: 10.1042/BST20210336. Biochem Soc Trans. 2022. PMID: 35579290 Review.
References
-
- Baulcombe D. RNA silencing in plants. Biochem (Lond) 2015;37:10–13. doi: 10.1042/BIO03702010. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

