Machine learning insights into thrombo-ischemic risks and bleeding events through platelet lysophospholipids and acylcarnitine species
- PMID: 38480746
- PMCID: PMC10937715
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-024-56304-x
Machine learning insights into thrombo-ischemic risks and bleeding events through platelet lysophospholipids and acylcarnitine species
Abstract
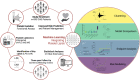
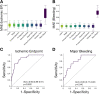
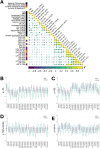
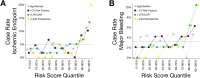
Coronary artery disease (CAD) often leads to adverse events resulting in significant disease burdens. Underlying risk factors often remain inapparent prior to disease incidence and the cardiovascular (CV) risk is not exclusively explained by traditional risk factors. Platelets inherently promote atheroprogression and enhanced platelet functions and distinct platelet lipid species are associated with disease severity in patients with CAD. Lipidomics data were acquired using mass spectrometry and processed alongside clinical data applying machine learning to model estimates of an increased CV risk in a consecutive CAD cohort (n = 595). By training machine learning models on CV risk measurements, stratification of CAD patients resulted in a phenotyping of risk groups. We found that distinct platelet lipids are associated with an increased CV or bleeding risk and independently predict adverse events. Notably, the addition of platelet lipids to conventional risk factors resulted in an increased diagnostic accuracy of patients with adverse CV events. Thus, patients with aberrant platelet lipid signatures and platelet functions are at elevated risk to develop adverse CV events. Machine learning combining platelet lipidome data and common clinical parameters demonstrated an increased diagnostic value in patients with CAD and might improve early risk discrimination and classification for CV events.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Large-scale lipidomics profiling reveals characteristic lipid signatures associated with an increased cardiovascular risk.Clin Res Cardiol. 2023 Nov;112(11):1664-1678. doi: 10.1007/s00392-023-02260-x. Epub 2023 Jul 20. Clin Res Cardiol. 2023. PMID: 37470807 Free PMC article.
-
Acute coronary syndrome is associated with a substantial change in the platelet lipidome.Cardiovasc Res. 2022 Jun 29;118(8):1904-1916. doi: 10.1093/cvr/cvab238. Cardiovasc Res. 2022. PMID: 34323932
-
Statin Treatment Is Associated with Alterations in the Platelet Lipidome.Thromb Haemost. 2023 Jun;123(6):585-596. doi: 10.1055/s-0043-1764353. Epub 2023 Mar 10. Thromb Haemost. 2023. PMID: 36898406
-
The influence of low-grade inflammation on platelets in patients with stable coronary artery disease.Thromb Haemost. 2015 Aug 31;114(3):519-29. doi: 10.1160/TH14-12-1007. Epub 2015 Jun 11. Thromb Haemost. 2015. PMID: 26062929 Review.
-
Benefits and risks of clopidogrel use in patients with coronary artery disease: evidence from randomized studies and registries.Clin Ther. 2008;30 Pt 2:2191-202. doi: 10.1016/j.clinthera.2008.12.001. Clin Ther. 2008. PMID: 19281914 Review.
Cited by
-
Reduced Platelet Aggregation and Plasma Cytokine Levels Mitigate Progressive Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease (MASLD).J Inflamm Res. 2025 Aug 20;18:11385-11400. doi: 10.2147/JIR.S533707. eCollection 2025. J Inflamm Res. 2025. PMID: 40860949 Free PMC article.
-
Novel 3-dimensional effective regurgitation orifice area quantification serves as a reliable tool to identify severe mitral valve regurgitation.Sci Rep. 2024 Sep 27;14(1):22067. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-73264-4. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39333219 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

