Protein Kinase A in neurological disorders
- PMID: 38481146
- PMCID: PMC10936040
- DOI: 10.1186/s11689-024-09525-0
Protein Kinase A in neurological disorders
Abstract
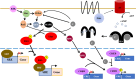
Cyclic adenosine 3', 5' monophosphate (cAMP)-dependent Protein Kinase A (PKA) is a multi-functional serine/threonine kinase that regulates a wide variety of physiological processes including gene transcription, metabolism, and synaptic plasticity. Genomic sequencing studies have identified both germline and somatic variants of the catalytic and regulatory subunits of PKA in patients with metabolic and neurodevelopmental disorders. In this review we discuss the classical cAMP/PKA signaling pathway and the disease phenotypes that result from PKA variants. This review highlights distinct isoform-specific cognitive deficits that occur in both PKA catalytic and regulatory subunits, and how tissue-specific distribution of these isoforms may contribute to neurodevelopmental disorders in comparison to more generalized endocrine dysfunction.
Keywords: CREB; Cognition; Endocrine Systems; Gene transcription; Kinases; Learning; MAPK; Memory; Metabolic Disorders; Movement Disorders; Neurodegeneration; Neurodevelopment; PKA; Protein phosphorylation; cAMP.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

