A case of severe Mycobacterium thermoresistibile pneumonia
- PMID: 38481423
- PMCID: PMC10937102
- DOI: 10.1002/rcr2.1308
A case of severe Mycobacterium thermoresistibile pneumonia
Abstract
Mycobacterium thermoresistibile is a thermotolerant nontuberculous mycobacterium which can rarely result in human infection. Although immunosuppression has been identified as a risk factor for infection, it is possible that mycobacterial laboratories may have previously under-recognized M. thermoresistibile as standard mycobacterial incubation temperatures are suboptimal for culture of this organism. Here, we present a case of severe M. thermoresistibile pneumonia associated with achalasia requiring life support in the intensive care unit. We speculated that the interplay between specific host and environmental risk factors contributed to acquisition of infection. Infection with this fastidious organism required prolonged treatment with multiple antimicrobials and adjunctive therapeutic drug monitoring which led to clinical cure despite residual lung injury. We also reviewed literature documenting cases of human infection with M. thermoresistibile. The diagnosis of M. thermoresistibile requires a high degree of clinical suspicion considering its association with immunosuppressive conditions, postulated environmental inoculation and eponymous culture growth characteristics.
Keywords: Mycobacterium thermoresistibile; achalasia; lung injury; rare lung diseases; respiratory infections (non‐tuberculous).
© 2024 The Authors. Respirology Case Reports published by John Wiley & Sons Australia, Ltd on behalf of The Asian Pacific Society of Respirology.
Conflict of interest statement
No conflicts of interest.
Figures
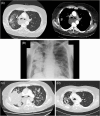
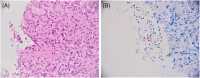
References
-
- Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute . Performance standards for susceptibility testing of mycobacteria, Nocardia spp., and other aerobic actinomycetes. 1st ed. CLSI document M62. Wayne, PA: Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute; 2018.
-
- Primm TPFJ. In: reference module in biomedical science [Internet]. Amsterdam (NL): Elsevier; 2014. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/B9780128012383030099
-
- Foster SF, Martin P, Davis W, Allan GS, Mitchell DH, Malik R. Chronic pneumonia caused by Mycobacterium thermoresistibile in a cat. J Small Anim Pract. 1999;40(9):433–438. - PubMed
-
- Neonakis IK, Gitti Z, Kontos F, Baritaki S, Petinaki E, Baritaki M, et al. Mycobacterium thermoresistibile: case report of a rarely isolated mycobacterium from Europe and review of literature. Indian J Med Microbiol. 2009;27(3):264–267. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

