The Role of Sodium-Glucose Cotransporter-2 Inhibitors in the Treatment Paradigm of CKD in Africa: An African Association of Nephrology Panel Position Paper
- PMID: 38481515
- PMCID: PMC10928012
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ekir.2023.12.019
The Role of Sodium-Glucose Cotransporter-2 Inhibitors in the Treatment Paradigm of CKD in Africa: An African Association of Nephrology Panel Position Paper
Keywords: Africa; CKD management; SGLT2i; chronic kidney disease; diabetic kidney disease; sodium-glucose cotransporter-2 inhibitors.
Figures
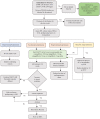
References
-
- KDIGO 2012 Clinical Practice Guideline for the Evaluation and Management of Chronic Kidney Disease. https://kdigo.org/wp-content/uploads/2017/02/KDIGO_2012_CKD_GL.pdf - PubMed
-
- The top 10 causes of death. World Health Organization. https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/the-top-10-causes-of-death
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

