Immunogenicity of chimeric hemagglutinins delivered by an orf virus vector platform against swine influenza virus
- PMID: 38482020
- PMCID: PMC10933025
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1322879
Immunogenicity of chimeric hemagglutinins delivered by an orf virus vector platform against swine influenza virus
Abstract
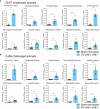
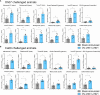
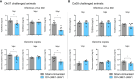
Orf virus (ORFV) is a large DNA virus that can harbor and efficiently deliver viral antigens in swine. Here we used ORFV as a vector platform to deliver chimeric hemagglutinins (HA) of Influenza A virus of swine (IAV-S). Vaccine development against IAV-S faces limitations posed by strain-specific immunity and the antigenic diversity of the IAV-S strains circulating in the field. A promising alternative aiming at re-directing immune responses on conserved epitopes of the stalk segment of the hemagglutinin (HA2) has recently emerged. Sequential immunization with chimeric HAs comprising the same stalk but distinct exotic head domains can potentially induce cross-reactive immune responses against conserved epitopes of the HA2 while breaking the immunodominance of the head domain (HA1). Here, we generated two recombinant ORFVs expressing chimeric HAs encoding the stalk region of a contemporary H1N1 IAV-S strain and exotic heads derived from either H6 or H8 subtypes, ORFVΔ121cH6/1 and ORFVΔ121cH8/1, respectively. The resulting recombinant viruses were able to express the heterologous protein in vitro. Further, the immunogenicity and cross-protection of these vaccine candidates were assessed in swine after sequential intramuscular immunization with OV-cH6/1 and OV-cH8/1, and subsequent challenge with divergent IAV-S strains. Humoral responses showed that vaccinated piglets presented increasing IgG responses in sera. Additionally, cross-reactive IgG and IgA antibody responses elicited by immunization were detected in sera and bronchoalveolar lavage (BAL), respectively, by ELISA against different viral clades and a diverse range of contemporary H1N1 IAV-S strains, indicating induction of humoral and mucosal immunity in vaccinated animals. Importantly, viral shedding was reduced in nasal swabs from vaccinated piglets after intranasal challenge with either Oh07 (gamma clade) or Ca09 (npdm clade) IAV-S strains. These results demonstrated the efficiency of ORFV-based vectors in delivering chimeric IAV-S HA-based vaccine candidates and underline the potential use of chimeric-HAs for prevention and control of influenza in swine.
Keywords: ORFV vectors; chimeric HA; cross-protection; swine influenza; vaccines.
Copyright © 2024 do Nascimento, de Oliveira, Butt and Diel.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors DD and GM declare that there is a patent pending related to this research U.S. Serial No. 63/433,242 and PCT International Application Serial No. PCT/US2023/84345. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest. The author(s) declared that they were an editorial board member of Frontiers, at the time of submission. This had no impact on the peer review process and the final decision.
Figures
References
-
- Friebe A, Siegling A, Friederichs S, Volk H-D, Weber O. Immunomodulatory effects of inactivated parapoxvirus ovis (ORF virus) on human peripheral immune cells: induction of cytokine secretion in monocytes and Th1-like cells. J Virol (2004) 78:9400–11. doi: 10.1128/JVI.78.17.9400-9411.2004 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

