Sudocetaxel Zendusortide (TH1902) triggers the cGAS/STING pathway and potentiates anti-PD-L1 immune-mediated tumor cell killing
- PMID: 38482021
- PMCID: PMC10936008
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1355945
Sudocetaxel Zendusortide (TH1902) triggers the cGAS/STING pathway and potentiates anti-PD-L1 immune-mediated tumor cell killing
Abstract
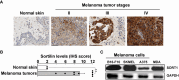
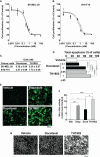
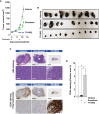
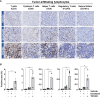
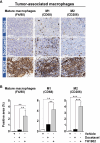
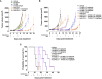
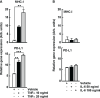
The anticancer efficacy of Sudocetaxel Zendusortide (TH1902), a peptide-drug conjugate internalized through a sortilin-mediated process, was assessed in a triple-negative breast cancer-derived MDA-MB-231 immunocompromised xenograft tumor model where complete tumor regression was observed for more than 40 days after the last treatment. Surprisingly, immunohistochemistry analysis revealed high staining of STING, a master regulator in the cancer-immunity cycle. A weekly administration of TH1902 as a single agent in a murine B16-F10 melanoma syngeneic tumor model demonstrated superior tumor growth inhibition than did docetaxel. A net increase in CD45 leukocyte infiltration within TH1902-treated tumors, especially for tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes and tumor-associated macrophages was observed. Increased staining of perforin, granzyme B, and caspase-3 was suggestive of elevated cytotoxic T and natural killer cell activities. Combined TH1902/anti-PD-L1 treatment led to increases in tumor growth inhibition and median animal survival. TH1902 inhibited cell proliferation and triggered apoptosis and senescence in B16-F10 cells in vitro, while inducing several downstream effectors of the cGAS/STING pathway and the expression of MHC-I and PD-L1. This is the first evidence that TH1902 exerts its antitumor activity, in part, through modulation of the immune tumor microenvironment and that the combination of TH1902 with checkpoint inhibitors (anti-PD-L1) could lead to improved clinical outcomes.
Keywords: PD-L1; STING; checkpoint inhibitor; docetaxel; immune tumor microenvironment; peptide-drug conjugate; sortilin.
Copyright © 2024 Demeule, Currie, Charfi, Zgheib, Cousineau, Lullier, Béliveau, Marsolais and Annabi.
Conflict of interest statement
This study received funding from Theratechnologies. The funder had the following involvement with the study : MD, JC-C, CC, AZ, RB, CM, and BA are listed as inventors on patent applications and were involved in study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish, and preparation of the manuscript. B.A. received research support from Theratechnologies. All authors declare no other competing interests.
Figures



References
-
- Charfi C, Demeule M, Currie JC, Larocque A, Zgheib A, Danalache BA, et al. . New peptide-drug conjugates for precise targeting of SORT1-mediated vasculogenic mimicry in the tumor microenvironment of TNBC-derived MDA-MB-231 breast and ovarian ES-2 clear cell carcinoma cells. Front Oncol (2021) 11:760787. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2021.760787 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

