Magnetic iron oxide-based nanozymes: from synthesis to application
- PMID: 38482039
- PMCID: PMC10929596
- DOI: 10.1039/d3na00903c
Magnetic iron oxide-based nanozymes: from synthesis to application
Abstract
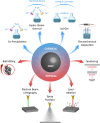
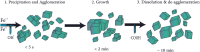
Iron oxide nanozymes (IONzymes) are a class of magnetic nanoparticles that mimic the enzymatic activity of natural enzymes. These particles have received significant attention in recent years due to their unique properties, such as high stability, tunable magnetic responsiveness, and ability to act as biocatalysts for various chemical reactions. In this review, we aim to provide an overview of the production methods of magnetic nanozymes, including chemical, physical, and biological synthesis. The structure and design of magnetic nanozymes are also discussed in detail, as well as their applications in various fields such as biomedicine and environmental science. The results of various studies and the latest advances in the field of magnetic nanozymes are also discussed. This review provides valuable insights into the current state of magnetic nanozymes and highlights their potential for further development and application in various fields.
This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts to declare.
Figures














References
-
- Sone B. T. Diallo A. Fuku X. G. Gurib-Fakim A. Maaza M. Biosynthesized CuO nano-platelets: Physical properties & enhanced thermal conductivity nanofluidics. Arabian J. Chem. 2020;13:160–170. doi: 10.1016/j.arabjc.2017.03.004. - DOI
-
- Ash A. Revati K. Pandey B. D. Microbial synthesis of iron-based nanomaterials – A review. Bull. Mater. Sci. 2011;34:191–198. doi: 10.1007/s12034-011-0076-6. - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

