Quality of life and quality of education among physiotherapy students in Europe
- PMID: 38482532
- PMCID: PMC10936755
- DOI: 10.3389/fmed.2024.1344028
Quality of life and quality of education among physiotherapy students in Europe
Erratum in
-
Corrigendum: Quality of life and quality of education among physiotherapy students in Europe.Front Med (Lausanne). 2024 Apr 8;11:1408214. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2024.1408214. eCollection 2024. Front Med (Lausanne). 2024. PMID: 38651059 Free PMC article.
Abstract
Background: The study of physiotherapy is challenging and can affect the students' well-being and quality of life. The aim of this study was to describe and compare factors that could affect well-being among students across Europe.
Methods: In this descriptive cross-sectional study using an online questionnaire survey, students of bachelor's physiotherapy programs from 23 European faculties, from 8 countries, were interviewed on mental health and stress burden, sleep quality, dietary habits, and physical activity.
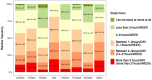
Results: Although 75% of students rated their quality of life positively and 47% were satisfied with their mental health, 65% showed higher levels of stress and 51% described impaired sleep quality. The minimum physical activity of 150 min weekly was described by 79% of students, within which 67% engaged in strengthening twice a week. Students with a higher stress load/worse psychological health also showed worse sleep quality and lower amount of physical activity, women were significantly worse off. In terms of physical activity and sleep quality, students from Finland and Kosovo achieved the best results, while students from Italy, Greece, and Portugal achieved the worst. Students from Italy indicated the greatest dissatisfaction with the organisation of the study system and communication with teachers, while in Kosovo students rated the communication and study organisation the highest. All students had a problem with adhering to nutritional habits. Students from Italy and Spain, with the lowest body mass indexes and weight averages, were closest to the nutrition recommendations.
Conclusion: We demonstrated that physiotherapy students are burdened with stress, suffer from sleep disorders, and do not follow the recommendations regarding nutrition nor physical activity. There are significant differences between universities and countries in some aspects.
Keywords: nutrition; physical activity; physiotherapy; sleep; stress; students.
Copyright © 2024 Schramlová, Řasová, Jonsdottir, Pavlíková, Rambousková, Äijö, Šlachtová, Kobesová, Žiaková, Kahraman, Pavlů, Bermejo-Gil, Bakalidou, Billis, Georgios, Alves-Guerreiro, Strimpakos, Příhoda, Kiviluoma-Ylitalo, Lähteenmäki, Koišová, Berisha, Hagovská, Arca and Cortés-Amaro.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Rasova K, Feys P, Henze T, Van Tongeren H, Cattaneo D, Jonsdottir J, et al. . Emerging evidence-based physical rehabilitation for multiple sclerosis – towards an inventory of current content across Europe. Health Qual Life Outcomes. (2010) 8:76. doi: 10.1186/1477-7525-8-76, PMID: - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Hodselmans AP, Hemdal E, Lundberg S, Bjarnegård A, Hobbelen H, Svantesson U. Physiotherapy students’ perceived stress, stressors, and reactions to stressors: a comparative study between Sweden and the Netherlands. Physiother Theory Pract. (2018) 34:293–300. doi: 10.1080/09593985.2017.1390805, PMID: - DOI - PubMed
-
- Wikström-Grotell C. Physiotherapy and physiotherapy education – from an international to a global and value-based perspective. Eur J Phys. (2021) 23:133–4. doi: 10.1080/21679169.2021.1907967 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources