Percutaneous Image-Guided Cryoablation of Endophytic Renal Cell Carcinoma
- PMID: 38483602
- PMCID: PMC10997531
- DOI: 10.1007/s00270-023-03633-5
Percutaneous Image-Guided Cryoablation of Endophytic Renal Cell Carcinoma
Abstract
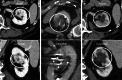
Purpose: Endophytic renal cancer treatment is a challenge. Due to difficulties in endophytic tumor visualization during surgical extirpation, image-guided percutaneous cryoablation (PCA) is an attractive alternative. The minimally invasive nature of PCA makes it favorable for comorbid patients as well as patients in which surgery is contraindicated. Oncological outcomes and complications after PCA of endophytic biopsy-proven renal cell carcinoma (RCC) were reviewed in this study.
Materials and methods: Patients were included after a multidisciplinary team conference from January 2015 to November 2021. Inclusion criteria were endophytic biopsy-proven T1 RCC treated with PCA with one year of follow-up. Complications were reported according to the Cardiovascular and Interventional Radiological Society of Europe (CIRSE) classification system and the Clavien-Dindo classification (CDC) system. Major complications were defined as a grade ≥ 3 according to the CDC.
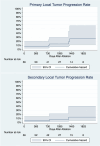
Results: Fifty-six patients were included with a total of 56 endophytic tumors treated during 61 PCA sessions. The median RENAL nephrometry score was 9 (IQR 2), and the mean tumor size was 25.7 mm (SD ± 8.9 mm). Mean hospitalization time was 0.39 (SD ± 1.1) days. At a mean follow-up of 996 days (SD ± 559), 86% of tumors were recurrence free after one PCA. No patients progressed to metastatic disease. According to the CIRSE classification, 10.7% (n = 6) had grade 3 complications, and 5.4% (n = 3) had CDC major complications.
Conclusion: This study demonstrates that PCA of endophytic biopsy-proven T1 RCC is safe with few major complications and excellent local tumor control rates at almost three-year mean follow-up. LEVEL OF EVIDENCE 3: Retrospective cohort study.
Keywords: Ablation; Cryoablation; Endophytic tumor; PCA; Percutaneous; RCC; Renal cancer.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Christian Greve Jensen, Marco Dybdahl, John Valtersson, Bo Redder Mussmann, Lars Lund, and Brian Welch have no conflict of interest. Louise Duus has received grant from Boehringer Ingelheim for attending the European Society of Thoracic Imaging (ESTI) Winter course 2022. Theresa Junker has received research grant from Boston Scientific. Pia Iben Pietersen has received grant from Boehringer Ingelheim for attending the European Society of Thoracic Imaging (ESTI) Winter course 2022. Ole Graumann has received speaker honoraria from Advisory Board member and received research grant from Boston Scientific.
Figures
References
-
- Junker T, Duus L, Rasmussen BSB, Azawi N, Lund L, Norgaard B, et al. Partial nephrectomy versus percutaneous cryoablation of small renal cell carcinomas: a comparison of complications in a prospective multicenter cohort study. J Vasc Interv Radiol. 2022 doi: 10.1016/j.jvir.2022.07.007. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

