Uncovering a hidden functional role of the XRE-cupin protein PsdR as a novel quorum-sensing regulator in Pseudomonas aeruginosa
- PMID: 38484003
- PMCID: PMC10965056
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1012078
Uncovering a hidden functional role of the XRE-cupin protein PsdR as a novel quorum-sensing regulator in Pseudomonas aeruginosa
Abstract
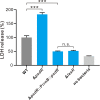
XRE-cupin family proteins containing an DNA-binding domain and a cupin signal-sensing domain are widely distributed in bacteria. In Pseudomonas aeruginosa, XRE-cupin transcription factors have long been recognized as regulators exclusively controlling cellular metabolism pathways. However, their potential functional roles beyond metabolism regulation remain unknown. PsdR, a typical XRE-cupin transcriptional regulator, was previously characterized as a local repressor involved solely in dipeptide metabolism. Here, by measuring quorum-sensing (QS) activities and QS-controlled metabolites, we uncover that PsdR is a new QS regulator in P. aeruginosa. Our RNA-seq analysis showed that rather than a local regulator, PsdR controls a large regulon, including genes associated with both the QS circuit and non-QS pathways. To unveil the underlying mechanism of PsdR in modulating QS, we developed a comparative transcriptome approach named "transcriptome profile similarity analysis" (TPSA). Using this TPSA method, we revealed that PsdR expression causes a QS-null-like transcriptome profile, resulting in QS-inactive phenotypes. Based on the results of TPSA, we further demonstrate that PsdR directly binds to the promoter for the gene encoding the QS master transcription factor LasR, thereby negatively regulating its expression and influencing QS activation. Moreover, our results showed that PsdR functions as a negative virulence regulator, as inactivation of PsdR enhanced bacterial cytotoxicity on host cells. In conclusion, we report on a new QS regulation role for PsdR, providing insights into its role in manipulating QS-controlled virulence. Most importantly, our findings open the door for a further discovery of untapped functions for other XRE-Cupin family proteins.
Copyright: © 2024 Qiu et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures


Similar articles
-
PqsE Expands and Differentially Modulates the RhlR Quorum Sensing Regulon in Pseudomonas aeruginosa.Microbiol Spectr. 2022 Jun 29;10(3):e0096122. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.00961-22. Epub 2022 May 23. Microbiol Spectr. 2022. PMID: 35604161 Free PMC article.
-
The Small RNA AmiL Regulates Quorum Sensing-Mediated Virulence in Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1.Microbiol Spectr. 2022 Apr 27;10(2):e0221121. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.02211-21. Epub 2022 Mar 9. Microbiol Spectr. 2022. PMID: 35262393 Free PMC article.
-
Transcription Inhibitors with XRE DNA-Binding and Cupin Signal-Sensing Domains Drive Metabolic Diversification in Pseudomonas.mSystems. 2021 Jan 12;6(1):e00753-20. doi: 10.1128/mSystems.00753-20. mSystems. 2021. PMID: 33436508 Free PMC article.
-
An evolving perspective on the Pseudomonas aeruginosa orphan quorum sensing regulator QscR.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2014 Oct 28;4:152. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2014.00152. eCollection 2014. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2014. PMID: 25389523 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Chemical probes of quorum sensing: from compound development to biological discovery.FEMS Microbiol Rev. 2016 Sep;40(5):774-94. doi: 10.1093/femsre/fuw009. Epub 2016 Jun 5. FEMS Microbiol Rev. 2016. PMID: 27268906 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
An anticipatory mechanism enhances the cooperative behaviors of quorum sensing mutants in Pseudomonas aeruginosa.PLoS Pathog. 2025 Apr 15;21(4):e1013046. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1013046. eCollection 2025 Apr. PLoS Pathog. 2025. PMID: 40233126 Free PMC article.
-
Co-regulation of cooperative and private traits by PsdR in Pseudomonas aeruginosa.Evol Lett. 2024 Dec 20;9(2):273-281. doi: 10.1093/evlett/qrae067. eCollection 2025 Apr. Evol Lett. 2024. PMID: 40191406 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Gellatly SL, Hancock RE (2013) Pseudomonas aeruginosa: new insights into pathogenesis and host defenses. Pathogens and disease 67: 159–173. - PubMed
-
- Schuster M, Greenberg EP (2006) A network of networks: quorum-sensing gene regulation in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. International journal of medical microbiology 296: 73–81. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

