Associations of Kidney Tubular Biomarkers With Incident Macroalbuminuria and Sustained Low eGFR in DCCT/EDIC
- PMID: 38484321
- PMCID: PMC11362110
- DOI: 10.2337/dc23-2196
Associations of Kidney Tubular Biomarkers With Incident Macroalbuminuria and Sustained Low eGFR in DCCT/EDIC
Abstract
Objective: Tubulointerstitial injury contributes to diabetic kidney disease (DKD) progression. We tested tubular biomarker associations with DKD development in type 1 diabetes (T1D).
Research design and methods: We performed a case-cohort study examining associations of tubular biomarkers, measured across seven time points spanning ∼30 years, with incident macroalbuminuria ("severely elevated albuminuria," urinary albumin excretion rate [AER] ≥300 mg/day) and sustained low estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) (persistent eGFR <60 mL/min/1.73 m2) in the Diabetes Control and Complications Trial (DCCT)/Epidemiology of Diabetes Interventions and Complications (EDIC) study. Biomarkers included KIM-1 and sTNFR1 in serum/plasma, MCP-1 and EGF in urine, and a composite tubular secretion score reflecting secreted solute clearance. We assessed biomarkers using single values, as mean values from consecutive time points, and as change over consecutive time points, each as time-updated exposures.
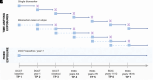
Results: At baseline, mean diabetes duration was 5.9 years, with mean HbA1c 8.9%, eGFR 125 mL/min/1.73 m2, and AER 16 mg/day. There were 4.8 and 3.5 cases per 1,000 person-years of macroalbuminuria and low eGFR, respectively. Assessed according to single biomarker values, KIM-1 was associated with risk of subsequent macroalbuminuria and low eGFR (hazard ratio [HR] per 20% higher biomarker 1.11 [95% CI 1.06, 1.16] and 1.12 [1.04, 1.21], respectively) and sTNFR1 was associated with subsequent macroalbuminuria (1.14 [1.03, 1.25]). Mean KIM-1 and EGF-to-MCP-1 ratio were associated with subsequent low eGFR. In slope analyses, increases in KIM-1 and sTNFR1 were associated with subsequent macroalbuminuria (per 20% biomarker increase, HR 1.81 [1.40, 2.34] and 1.95 [1.18, 3.21]) and low eGFR (2.26 [1.65, 3.09] and 2.94 [1.39, 6.23]).
Conclusions: Serial KIM-1 and sTNFR1 are associated with incident macroalbuminuria and sustained low eGFR in T1D.
© 2024 by the American Diabetes Association.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Bakris GL, Molitch M. Are all patients with type 1 diabetes destined for dialysis if they live long enough? Probably not. Diabetes Care 2018;41:389–390 - PubMed
-
- Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes (KDIGO) Diabetes Work Group . KDIGO 2022 clinical practice guideline for diabetes management in chronic kidney disease. Kidney Int 2022;102(5S):S1–S127 - PubMed
-
- Tuttle KR, Agarwal R, Alpers CE, et al. Molecular mechanisms and therapeutic targets for diabetic kidney disease. Kidney Int 2022;102:248–260 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 1993-2007/the National Eye Institute, the National Institute of Neurologic Disorders and Stroke, the General Clinical Research Centers Program
- UL1 TR002384/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- K23 DK135789/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- 1982-1993/Division of Diabetes Endocrinology and Metabolic Diseases of the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Disease
- U01 DK094176/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

