Modified FOLFOX6 plus bevacizumab with and without nivolumab for first-line treatment of metastatic colorectal cancer: phase 2 results from the CheckMate 9X8 randomized clinical trial
- PMID: 38485190
- PMCID: PMC10941175
- DOI: 10.1136/jitc-2023-008409
Modified FOLFOX6 plus bevacizumab with and without nivolumab for first-line treatment of metastatic colorectal cancer: phase 2 results from the CheckMate 9X8 randomized clinical trial
Abstract
Background: Standard first-line therapies for metastatic colorectal cancer (mCRC) include fluoropyrimidine-containing regimens with oxaliplatin and/or irinotecan and a biologic agent. Immunotherapy may enhance antitumor activity in combination with standard therapies in patients with mCRC. Here, we present phase 2 results of nivolumab plus standard-of-care therapy (SOC; 5-fluorouracil/leucovorin/oxaliplatin/bevacizumab) versus SOC in the first-line treatment of patients with mCRC (CheckMate 9X8).
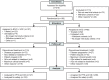
Methods: CheckMate 9X8 was a multicenter, open-label, randomized, phase 2/3 trial. Eligible patients were at least 18 years of age with unresectable mCRC and no prior chemotherapy for metastatic disease. Patients were randomized 2:1 to receive nivolumab 240 mg plus SOC or SOC alone every 2 weeks. The primary endpoint was progression-free survival (PFS) by blinded independent central review (BICR) per Response Evaluation Criteria in Solid Tumors V.1.1. Secondary endpoints included PFS by investigator assessment; objective response rate (ORR), disease control rate, duration of response, and time to response, all by BICR and investigator assessments; overall survival; and safety. Preplanned exploratory biomarker analyses were also performed.
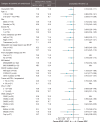
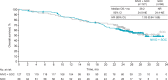
Results: From February 2018 through April 2019, 310 patients were enrolled, of which 195 patients were randomized to nivolumab plus SOC (n=127) or SOC (n=68). At 21.5-month minimum follow-up, PFS with nivolumab plus SOC versus SOC did not meet the prespecified threshold for statistical significance; median PFS by BICR was 11.9 months in both arms (HR, 0.81 (95% CI, 0.53 to 1.23); p=0.30). Higher PFS rates after 12 months (18 months: 28% vs 9%), higher ORR (60% vs 46%), and durable responses (median 12.9 vs 9.3 months) were observed with nivolumab plus SOC versus SOC. Grade 3-4 treatment-related adverse events were reported in 75% versus 48% of patients; no new safety signals were identified.
Conclusions: The CheckMate 9X8 trial investigating first-line nivolumab plus SOC versus SOC in patients with mCRC did not meet its primary endpoint of PFS by BICR. Nivolumab plus SOC showed numerically higher PFS rates after 12 months, a higher response rate, and more durable responses compared with SOC alone, with acceptable safety. Further investigation to identify subgroups of patients with mCRC that may benefit from nivolumab plus SOC versus SOC in the first-line setting is warranted.
Trial registration number: NCT03414983.
Keywords: gastrointestinal neoplasms; immune checkpoint inhibitors; immunotherapy; nivolumab; tumor biomarkers.
© Author(s) (or their employer(s)) 2024. Re-use permitted under CC BY-NC. No commercial re-use. See rights and permissions. Published by BMJ.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: H-JL reports consulting or advisory roles for Bayer, Bristol Myers Squibb, GlaxoSmithKline, Merck Serono, and Roche; honoraria from Bayer, Boehringer Ingelheim, Fulgent Genetics, GlaxoSmithKline, G1 Therapeutics, Isofol Medical, Jazz Pharmaceuticals, Merck Serono, Oncocyte, and Roche; travel, accommodations, and expenses from Bayer and Merck Serono. AP reports equity in C2i Genomics; advisor/consultant roles for Eli Lilly, Pfizer, Inivata, Biofidelity, Natera, Checkmate Pharmaceuticals, FMI, Guardant, AbbVie, Bayer, and Taiho; served on the DSMC for a Roche study; and has received research funding to the institution from PureTech, PMV Pharmaceuticals, Plexxicon, Takeda, Bristol Myers Squibb, Mirati Therapeutics, Novartis, Genentech, Natera, and Daiichi Sankyo. DRS reports consulting or advisory roles for Amgen, AstraZeneca, Bayer, Bristol Myers Squibb, Curio Science, EMD Serono, Evelo Therapeutics, Evidera, Exelixis, Genentech/Roche, GlaxoSmithKline, Intellisphere, Ipsen, Janssen, Jazz Pharmaceuticals, Eli Lilly, Mirati Therapeutics, Molecular Templates, Novartis, Novocure, Pfizer, Puma Biotechnology, Regeneron, Sanofi/Aventis, and Takeda; leadership roles at ASCO; travel, accommodations, and expenses from AstraZeneca, Genentech, and Novartis; and has received research funding to institution from Aeglea Biotherapeutics, Agios, Apollomics, Arcus Biosciences, Arrys Therapeutics, Astellas Pharma, AstraZeneca, Bayer, BeiGene, BIND Therapeutics, BioNTech, Blueprint Medicines, Boehringer Ingelheim, Bristol Myers Squibb, Calithera Biosciences, Celgene, Celldex, Clovis Oncology, Cyteir Therapeutics, Daiichi Sankyo, Denovo Biopharma, Eisai, Elevation Oncology, EMD Serono, G1 Therapeutics, Genentech/Roche, GlaxoSmithKline, GRAIL, Hutchison MediPharma, ImClone Systems, Immunogen, Incyte, Ipsen, Janssen Oncology, Kronos Bio, Eli Lilly, Loxo, Macrogenics, MedImmune, Merck, Molecular Partners, Molecular Templates, Nektar, Neon Therapeutics, Novartis, Novocure, Oncologie, Pfizer, PTC Therapeutics, PureTech, Razor Genomics, Repare Therapeutics, Rgenix, Takeda, Tesaro, Tizona Therapeutics Inc., Transgene, University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center – Simmons Cancer Center, and Verastem. ALC reports honoraria from Amgen; and has provided expert testimony for the Department of Justice. TY reports honoraria from Chugai Pharmaceuticals, Merck, Bayer Yakuhin, Ono Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd, Eli Lilly, and Taiho Pharmaceuticals; and research funding from Chugai Pharmaceuticals, Merck Sharp & Dohme Corporation, Daiichi Sankyo, Parexel, Ono Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd, Taiho Pharmaceuticals, Amgen, and Sanofi. EE reports honoraria from Servier, Array Biopharma, Roche, Bristol Myers Squibb, Merck Serono, and Sanofi/Aventis; honoraria from Boehringer Ingelheim, Amgen, GlaxoSmithKline, AbbVie/Genetech, Novartis, MSD, and AstraZeneca (to institution); consulting and advisory roles for Array BioPharma, Bristol Myers Squibb, Roche, Servier, Sanofi, Amgen, Merck Serono, and Bayer; research funding from Merck Serono and Amgen; and research funding (to institution) from Sanofi/Aventis, Servier, Bristol Myers Squibb, Array BioPharma, Roche, Pierre Fabre, and MedImmune; and travel and accommodations from Servier. DD reports consulting roles for Bayer, Promega, Array Biopharma, Eli Lilly, and Pfizer; and research funding from Merck, Bristol Myers Squibb, Genentech, Revolution Medicines, Millenium Pharmaceuticals, and Bayer. EC reports honoraria from Eisai and Bayer; and research funding from Bristol Myers Squibb, Merck, Novartis, Boston Biomedical, AstraZeneca, and Zymeworks. AM reports consulting or advisory roles for QED Therapeutics; honoraria from Eisai; and research funding from Taiho Pharmaceuticals. EB-B was an employee of Bristol Myers Squibb at the time of the study and reports consulting or advisory roles for Bristol Myers Squibb, Fennec Pharmaceuticals, Green3Bio, Geistlich Pharma, Oncternal Therapeutics, and Shasqi Inc; leadership roles in Catalyst Clinical Research; travel, accommodations, and expenses from Geistlich Pharma; and stock and other ownership interests in Oncternal Therapeutics and Catalyst Clinical Research. TK reports being an employee of Bristol Myers Squibb. DC, ABH, and JY report being employees of and owning stock in Bristol Myers Squibb. JT reports consulting roles for Array Biopharma, AstraZeneca, Bayer, Boehringer Ingelheim, Chugai, Daiichi Sankyo, F. Hoffmann-La Roche Ltd, Genentech Inc, HalioDX SAS, Hutchison MediPharma International, Ikena Oncology, Inspirna Inc, IQVIA, Lilly, Menarini, Merck Serono, Merus, MSD, Mirati, Neophore, Novartis, Ona Therapeutics, Orion Biotechnology, Peptomyc, Pfizer, Pierre Fabre, Samsung Bioepis, Sanofi, Scandion Oncology, Scorpion Therapeutics, Seattle Genetics, Servier, Sotio Biotech, Taiho, Tessa Therapeutics, and TheraMyc; stocks from Oniria Therapeutics; and educational collaboration with Imedex/HMP, Medscape Education, MJH Life Sciences, PeerView Institute for Medical Education, and Physicians Education Resource (PER). All other authors report no conflicts of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Grapsa D, Syrigos K, Saif MW. Bevacizumab in combination with fluoropyrimidine-irinotecan- or fluoropyrimidine-oxaliplatin-based chemotherapy for first-line and maintenance treatment of metastatic colorectal cancer. Expert Rev Anticancer Ther 2015;15:1267–81. 10.1586/14737140.2015.1102063 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Venook AP, Niedzwiecki D, Lenz H-J, et al. . Effect of first-line chemotherapy combined with cetuximab or bevacizumab on overall survival in patients with KRAS wild-type advanced or metastatic colorectal cancer: a randomized clinical trial. JAMA 2017;317:2392–401. 10.1001/jama.2017.7105 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
