Ultra-fast switching memristors based on two-dimensional materials
- PMID: 38485722
- PMCID: PMC10940724
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-024-46372-y
Ultra-fast switching memristors based on two-dimensional materials
Abstract
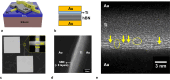
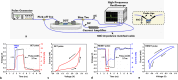
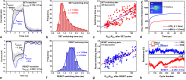
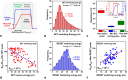
The ability to scale two-dimensional (2D) material thickness down to a single monolayer presents a promising opportunity to realize high-speed energy-efficient memristors. Here, we report an ultra-fast memristor fabricated using atomically thin sheets of 2D hexagonal Boron Nitride, exhibiting the shortest observed switching speed (120 ps) among 2D memristors and low switching energy (2pJ). Furthermore, we study the switching dynamics of these memristors using ultra-short (120ps-3ns) voltage pulses, a frequency range that is highly relevant in the context of modern complementary metal oxide semiconductor (CMOS) circuits. We employ statistical analysis of transient characteristics to gain insights into the memristor switching mechanism. Cycling endurance data confirms the ultra-fast switching capability of these memristors, making them attractive for next generation computing, storage, and Radio-Frequency (RF) circuit applications.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Talib MA, Majzoub S, Nasir Q, Jamal D. A systematic literature review on hardware implementation of artificial intelligence algorithms. J. Supercomput. 2021;77:1897–1938. doi: 10.1007/s11227-020-03325-8. - DOI
-
- Capra M, et al. An updated survey of efficient hardware architectures for accelerating deep convolutional neural networks. Future Internet. 2020;12:113. doi: 10.3390/fi12070113. - DOI
-
- Stoica, I. et al. A Berkeley view of systems challenges for Preprint at https://arxiv.org/abs/1712.05855 (2017).
-
- Fan X, et al. Flexible and wearable power sources for next‐generation wearable electronics. Batteries Supercaps. 2020;3:1262–1274. doi: 10.1002/batt.202000115. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

