Emergency airway management in resource limited setting
- PMID: 38486140
- PMCID: PMC10938719
- DOI: 10.1186/s12245-024-00607-3
Emergency airway management in resource limited setting
Abstract
Background: Emergency airway management in resource-limited settings presents multifaceted challenges due to shortages in essential medical resources, healthcare professionals, and infrastructure.
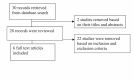
Methods: We conducted a literature search using keywords "Emergency Airway Management" "Low Resource" "Africa" "Asia" from databases such as Pubmed, and Google Scholar, from where we extracted relevant literature for our study.
Findings: These limitations resulted in delayed interventions, suboptimal care, and higher complication rates during intubation procedures. However, innovative solutions have emerged to address these challenges, including cost-effective airway management devices and training programs tailored for non-medical personnel. Capacity building and local empowerment are critical components of improving emergency airway management in these settings. Additionally, advocating for policy support and investment in healthcare infrastructure is essential to ensure access to essential equipment and adequate staffing. Collaboration and knowledge-sharing networks among healthcare professionals and organisations are pivotal in disseminating best practices and advancing healthcare delivery in resource-limited regions.
Conclusion: Future efforts should focus on tailored training programs, rigorous research, innovative device development, telemedicine solutions, sustainable capacity building, and advocacy to enhance emergency airway management in resource-limited settings.
Keywords: Emergency airway management; Resource-limited settings.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The future of Cochrane Neonatal.Early Hum Dev. 2020 Nov;150:105191. doi: 10.1016/j.earlhumdev.2020.105191. Epub 2020 Sep 12. Early Hum Dev. 2020. PMID: 33036834
-
An Innovative Inexpensive Portable Pulmonary Edema Intubation Simulator.J Educ Teach Emerg Med. 2020 Apr 15;5(2):I9-I20. doi: 10.21980/J8MM1R. eCollection 2020 Apr. J Educ Teach Emerg Med. 2020. PMID: 37465400 Free PMC article.
-
Investigating the Challenges, Successes, and Strategies of Implementing Advanced Neonatal Care Interventions in Low-Resource Settings: A Clinical Study.J Pharm Bioallied Sci. 2024 Jul;16(Suppl 3):S2839-S2841. doi: 10.4103/jpbs.jpbs_459_24. Epub 2024 Jul 31. J Pharm Bioallied Sci. 2024. PMID: 39346329 Free PMC article.
-
Healthcare stakeholders' perceptions and experiences of factors affecting the implementation of critical care telemedicine (CCT): qualitative evidence synthesis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Feb 18;2(2):CD012876. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD012876.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021. PMID: 33599282 Free PMC article.
-
Review of Manpower Management in Healthcare System: Strategies, Challenges, and Innovations.J Multidiscip Healthc. 2024 Nov 19;17:5341-5351. doi: 10.2147/JMDH.S497932. eCollection 2024. J Multidiscip Healthc. 2024. PMID: 39588490 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Preventing and Managing Tracheostomy-Related Emergencies in the Radiology Suite: Best Practices for Safety and Preparedness.J Radiol Nurs. 2025 Jun;44(2):150-160. doi: 10.1016/j.jradnu.2025.03.004. Epub 2025 Jun 3. J Radiol Nurs. 2025. PMID: 40486202
References
-
- World Bank. World Bank Country and Lending Groups. [Online]. Available at: https://datahelpdesk.worldbank.org/knowledgebase/articles/906519-world-b...~:text=For%20the%20current%202024%20fiscal,those%20with%20a%20GNI%20per (Accessed: January 15, 2024).
-
- Hamal PK. Airway Management in Low Resource settings. In: Ubaradka RS, Gupta N, Bidkar PU, Tripathy DK, Gupta A, editors. The Airway Manual. Singapore: Springer; 2023.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources